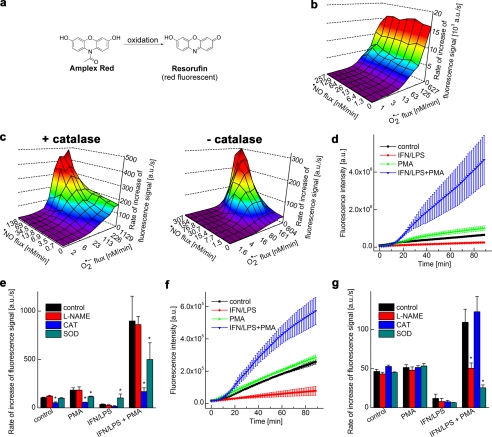
FIGURE 6.
Global profiling of H2O2 and ONOO−-derived oxidants by monitoring the oxidation of Amplex® Red. a, scheme showing oxidation of Amplex® Red to a red fluorescent product, resorufin. b, increase in the fluorescence intensity (due to resorufin, excitation at 535 nm, emission at 595 nm) caused by HRP-dependent oxidation of Amplex® Red (20 μm) in phosphate buffer in the presence of co-generated •NO and O2˙̄. a.u., arbitrary units. c, same as b except that HRP was not present. Note that the fluorescence intensity was greatly reduced as compared with b. d, oxidation of Amplex® Red (50 μm) by activated macrophages in the presence of HRP was measured. Increase in the fluorescence intensity was monitored in a fluorescence plate reader from incubations containing RAW 264.7 macrophages activated by different stimulators as shown. e, conditions were the same as in d except that the rate of increase in fluorescence intensity was measured in the presence of l-NAME and O2˙̄- and H2O2-detoxifying enzymes. CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase. f, same as d but in the absence of HRP. Note the decrease in the fluorescence intensity of the product. g, same as f but in the presence of l-NAME and O2˙̄- and H2O2-detoxifying enzymes. *, p < 0.05.