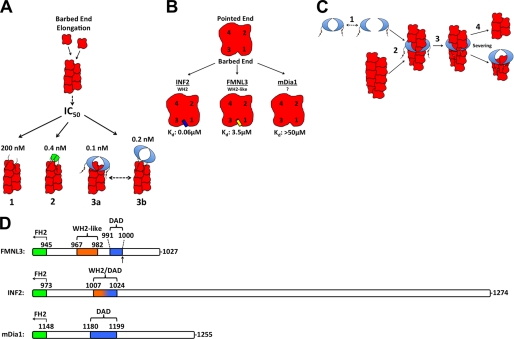
FIGURE 9.
Contributions of the FMNL3 C terminus to actin binding and actin filament severing. A, comparison of the observed effects of FMNL3 Cterm (1), GST-FMNL3 Cterm (2), and FMNL3 FH2-C (3) on barbed end elongation. FMNL3 FH2-C has two possible barbed end binding states, FH2-bound and Cterm-bound. B, comparison of actin monomer affinity of FMNL3-Cterm with the C termini of INF2 and mDia1. The proposed binding interface of FMNL3 and INF2 Cterm is positioned in the cleft at the barbed end of the actin monomer, located between subdomains 1 and 3. The binding site of mDia1-Cterm is unknown. C, proposed mechanism of filament severing by FMNL3-FFC. FH2 dimer dissociates (1), allowing filament side binding by the FH2 domain (2), which enables binding by the cis Cterm to subunits adjacent to those binding the FH2, destabilizing the filament (3), and ultimately resulting in severing (4). Barbed end affinity of the FH2 causes it to remain with the barbed end of the newly severed filament. D, comparison of the C termini from mouse FMNL3, INF2 (CAAX variant), and mDia1. Schematic alignments are based on the last 10 residues of their FH2 domains. The DAD boundaries represent the “core DAD” regions for FMNL3 and INF2 and extend to the basic residues in mDia1 (5). The arrow in FMNL3 denotes the site of splice variation after T999.