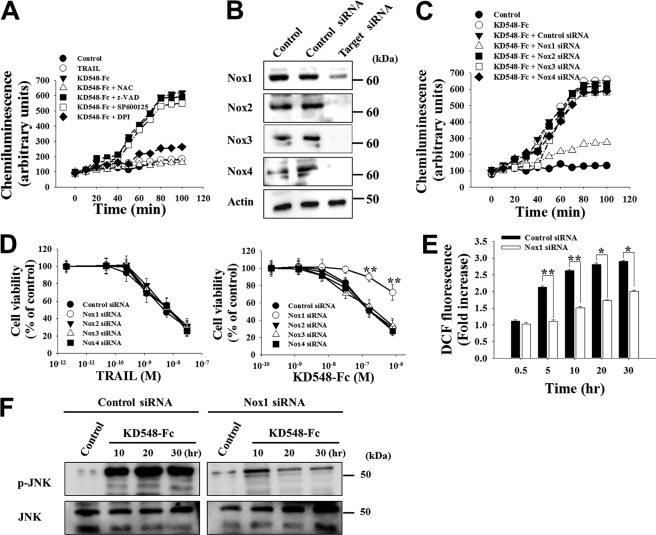
FIGURE 3.
KD548-Fc activates Nox1 NADPH oxidase to produce superoxide anion, leading to intracellular ROS accumulation, sustained JNK activation, and eventual apoptotic cell death in HeLa cells. A, superoxide anion generation assay of the cells left untreated (control) or treated with TRAIL (30 nm) or KD548-Fc (0.8 μm) in the absence or presence of the indicated chemicals. The data are representative of three separate experiments with the same results. B, Western blots showing the knockdown of Nox1, Nox2, Nox3, or Nox4 expression by siRNA transfection into HeLa cells. Control, untransfected cells. C and D, effects of knockdown of Nox1, Nox2, Nox3, or Nox4 on superoxide anion generation (C) and cell viability (D) in the cells, left untreated (control) or treated with KD548-Fc (C and D) or TRAIL (D). C, cells were treated with 0.8 μm of KD548-Fc. D, cells transfected with siRNA for 36 h were further incubated with the indicated concentrations of KD548-Fc or TRAIL for 40 h. E and F, effect of Nox1 knockdown on ROS production (E) or JNK phosphorylation (F) in the cells, untreated (control) or treated with KD548-Fc (0.8 μm) for the indicated periods. D and E, data represent mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 compared with the cells transfected with control siRNA.