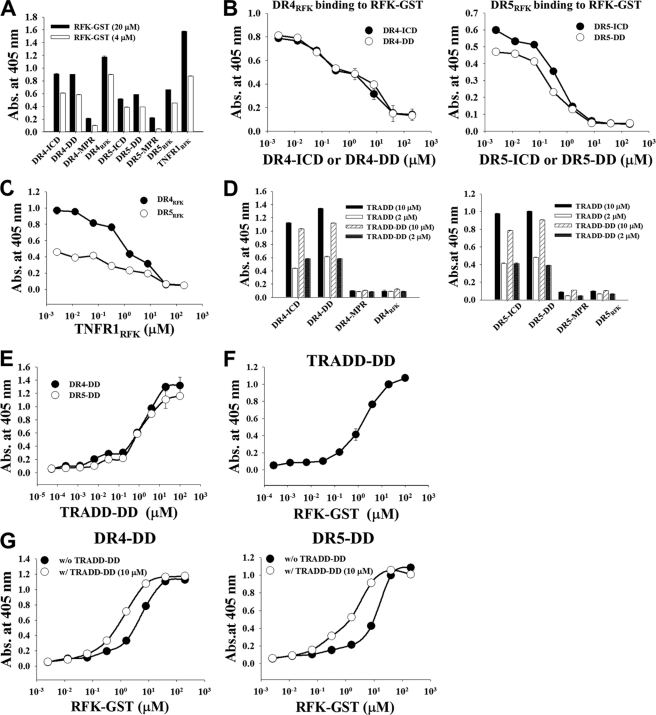
FIGURE 6.
DR4 and DR5 interact with RFK through the RFK-binding regions within the DDs to form the DR4/DR5-RFK complex, which is stabilized by the presence of TRADD. A, binding activity of RFK-GST (4 or 20 μm) for plate-coated intracellular fragments of DR4 and DR5, analyzed by ELISA. For a detailed description of each fragment, see supplemental Fig. S6. B and C, competition ELISA. B, binding activity of DR4RFK (30 μm) and DR5RFK (30 μm) for plate-coated RFK-GST was assessed in the presence of serially diluted DR4-ICD or DR4-DD and DR5-ICD or DR5-DD, respectively. C, binding activity of DR4RFK (30 μm) and DR5RFK (30 μm) for plate-coated RFK-GST was assessed in the presence of serially diluted TNFR1RFK. D, binding activity of TRADD or TRADD-DD (2 or 10 μm) to plate-coated intracellular fragments of DR4 and DR5. E–G, direct ELISA. E, binding activity of TRADD-DD to plate-coated DR4-DD or DR5-DD. F, binding activity of RFK-GST to plate-coated TRADD-DD. G, binding activity of RFK-GST to plate-coated DR4-DD or DR5-DD in the absence or presence of 10 μm TRADD-DD. A–G, data represent mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate.