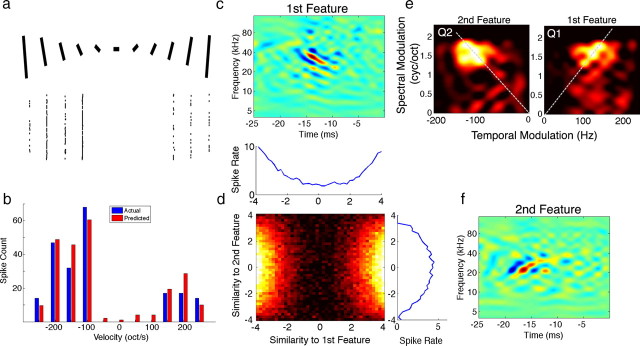
Figure 6.
Opponent features for spectral motion selectivity. a and b are as described in Figure 5. c, f, The most informative features extracted from responses to natural stimuli showed selectivity for opposing FM directions. d, While both features had a symmetric nonlinearity, the nonlinearity of the second feature was actually suppressive, reducing the response to the upward (nonpreferred) direction as shown in the full 2D nonlinearity. e, Decomposing each feature into its ripple components via a Fourier transform shows that each feature has power within a similar range of spectral and temporal modulations but in opposing quadrants. Furthermore, both features were tuned to the same velocity of 93 oct/s in opposing directions as indicated by the dashed lines.