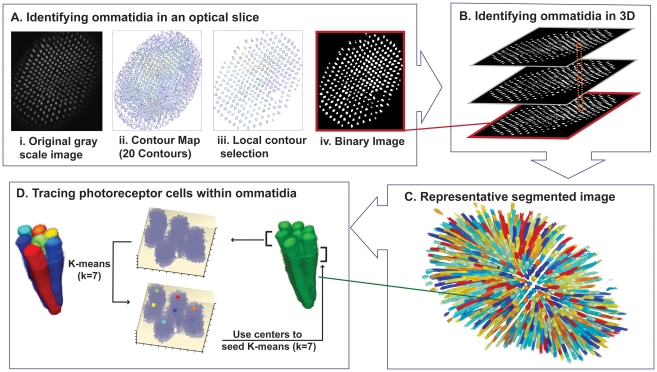
Figure 3. Image analysis methods to identify ommatidia and individual PRs.
(A) Step 1 – Identifying ommatidia in an optical slice. Each optical section is thresholded using local contour selection. i. a representative gray scale optical section; ii. a contour map of this image, where 20 intensity contour levels are drawn; iii. results of contour selection around a region; iv. the resulting binary image. (B) Step 2 – Identifying ommatidia in 3D. Filament finding in three dimensions is applied by searching in five consecutive slices for overlapping pixels, and growing the overlapping regions in subsequent slices. (C) Representative segmented image that results from steps 1 and 2. (D) Step 3 – Tracing PR cells within ommatidia. A representative ommatidium, extracted from the retina. Choosing the top 800 most intense points in the first five slices, k-means clustering is performed to identify 7 clusters, corresponding to the 7 PRs in each slice. Using these centers as seeds, we shift the window of five slices by one slice and perform k-means of the top 800 most intense points. This process is continued until the PRs are traced. Representative results are depicted on the left of the panel where each color identifies a different cell.