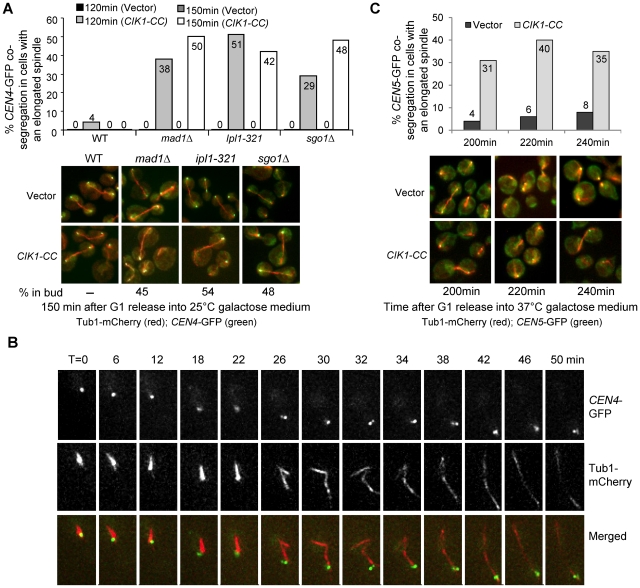
Figure 4. Overexpression of CIK1-CC results in syntelic attachment.
A. Mutants in the spindle or the tension checkpoint lead to chromosome mis-segregation in cells overexpressing CIK1-CC. A vector or a PGALCIK1-CC plasmid was introduced into WT, mad1Δ, ipl1-321, and sgo1Δ cells with CEN4-GFP TUB1-mCherry. The transformants were first arrested in G1 phase and then released into galactose medium at 25°C. Cells were collected at 120 and 150 min and fixed for the examination of fluorescence signals. The percentage of cells with mis-segregated sister CEN4-GFPs among those with an elongated spindle is shown in the upper panel (n>100). The localization of CEN4-GFP as well as spindle morphology in some representative cells is shown in the bottom panel. The numbers at the bottom of the images represent the percentage of cells that show GFP signal in the daughter cell among all of those with mis-segregated CEN4-GFP (n>100). B. Live-cell image of the segregation of CEN4-GFP in a sgo1Δ cell overexpressing CIK1-CC. sgo1Δ CEN4-GFP TUB1-mCherry cells with vectors or PGALCIK1-CC plasmids were arrested in G1 in raffinose medium. After release into galactose medium for 2 hr, the cells were spotted onto the surface of a slide covered with agarose medium (galactose) and subjected to live-cell microscopy. At each time point, a Z-stack with 8 planes, separated by 0.5 µm, was acquired and subsequently projected. C. The segregation of CEN5-GFP in mcd1-1 cohesin mutant cells after CIK1-CC overexpression. mcd1-1 TUB1-mCherry CEN5-GFP with either a vector or a PGALCIK1-CC plasmid were arrested in G1 phase in raffinose medium at 25°C and then released into 37°C galactose medium. We collected cells at 200, 220, and 240 min when majority of the cells were large budded to examine the spindle morphology and the segregation of CEN5-GFP. The percentage of CEN5-GFP co-segregation in cells with an elongated spindle is shown on the top (n>100). The localization of CEN5-GFP as well as spindle morphology in some representative cells is shown at the bottom panel.