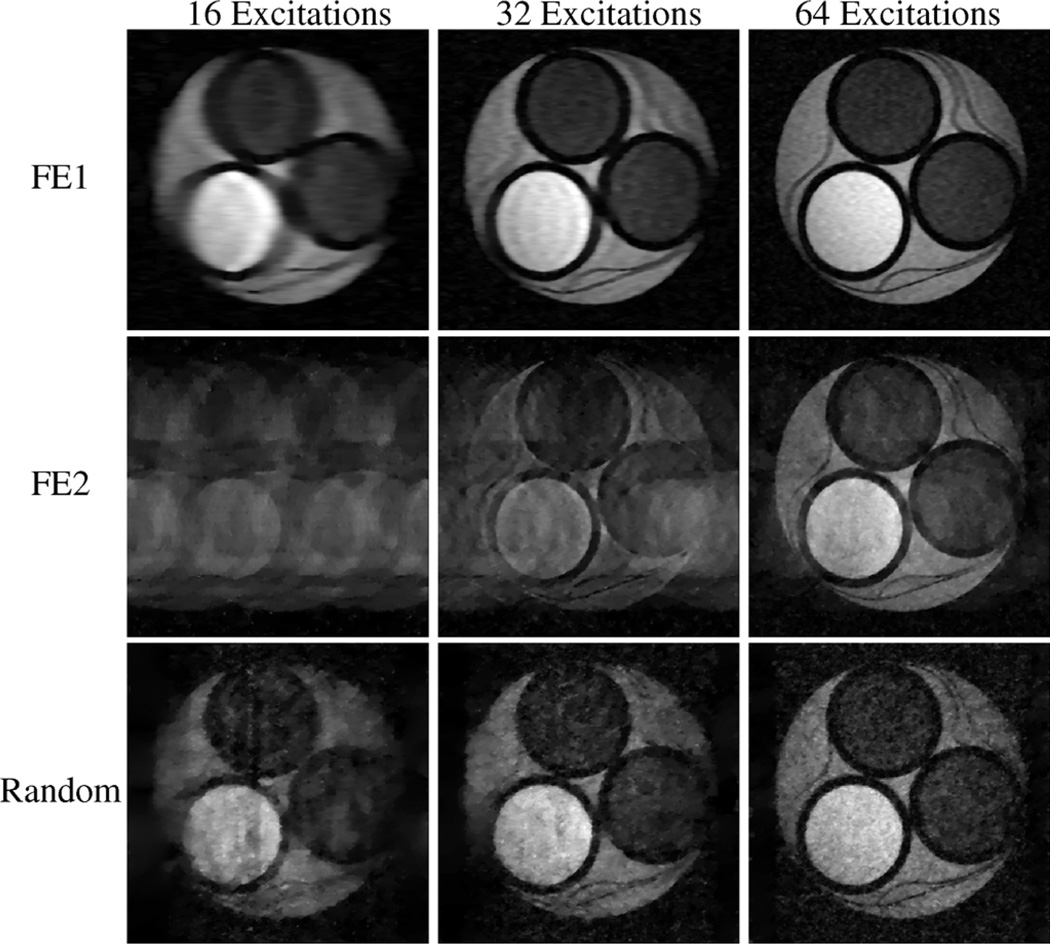
Fig. 3.
CS-MRI reconstructions from real experimental data from the compartmental phantom. Each row represents a different encoding scheme, while each column represents a different amount of measured data. These reconstructions demonstrate that CS-MRI with random encoding is feasible, and has different characteristics than either FE1 (which samples low-frequency k-space) or FE2 (which uses randomized k-space phase-encoding locations).