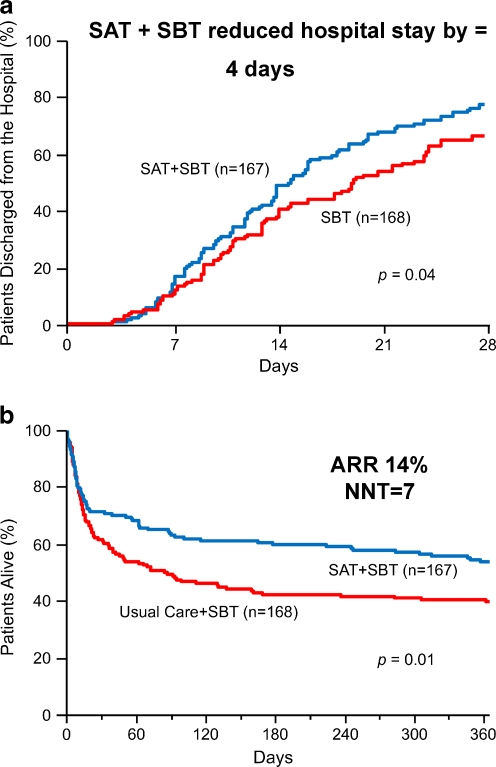
Fig. 3.
(a) The Awakening and Breathing Controlled (ABC) trial reduced intensive care unit stay (not shown) and hospital length of stay for mechanically ventilated patients by 4 days when daily spontaneous awakening trials (SATs) were paired with daily spontaneous breathing trials (SBTs) compared to the control group with sedation per usual care plus daily SBT. Adapted from Girard TD, et al. [54]. (b) The ABC trial was the first randomized controlled trial of any “weaning” component of critical care (i.e., the “back end of critical care”) to demonstrate that pairing spontaneous awakening trials (SATs) with spontaneous breathing trials (SBTs) increased survival, and the number needed to treat to save 1 life was 7. Adapted from Girard TD, et al. [54]