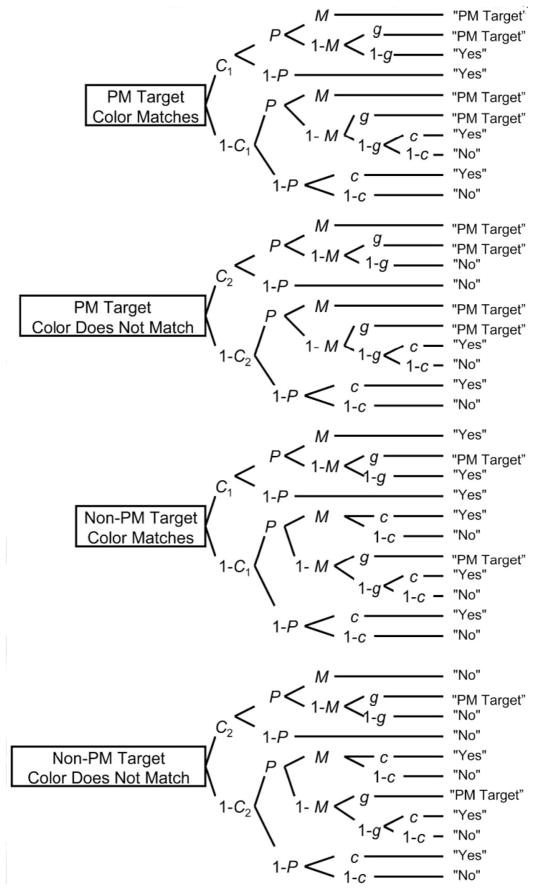
Figure 1.
Multinomial model of event-based prospective memory. Taken from “The source of adult age differences in event-based prospective memory: A multinomial modeling approach” by R. E. Smith and U. J. Bayen, 2006, Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32(3), p. 634. PM = prospective memory; P = probability of engaging in preparatory attentional processes; M = probability to discriminating between targets and non-targets; g = probability of guessing that a color matches; C1 = probability of detecting a color match; C2 = probability of detecting that a color does not match.