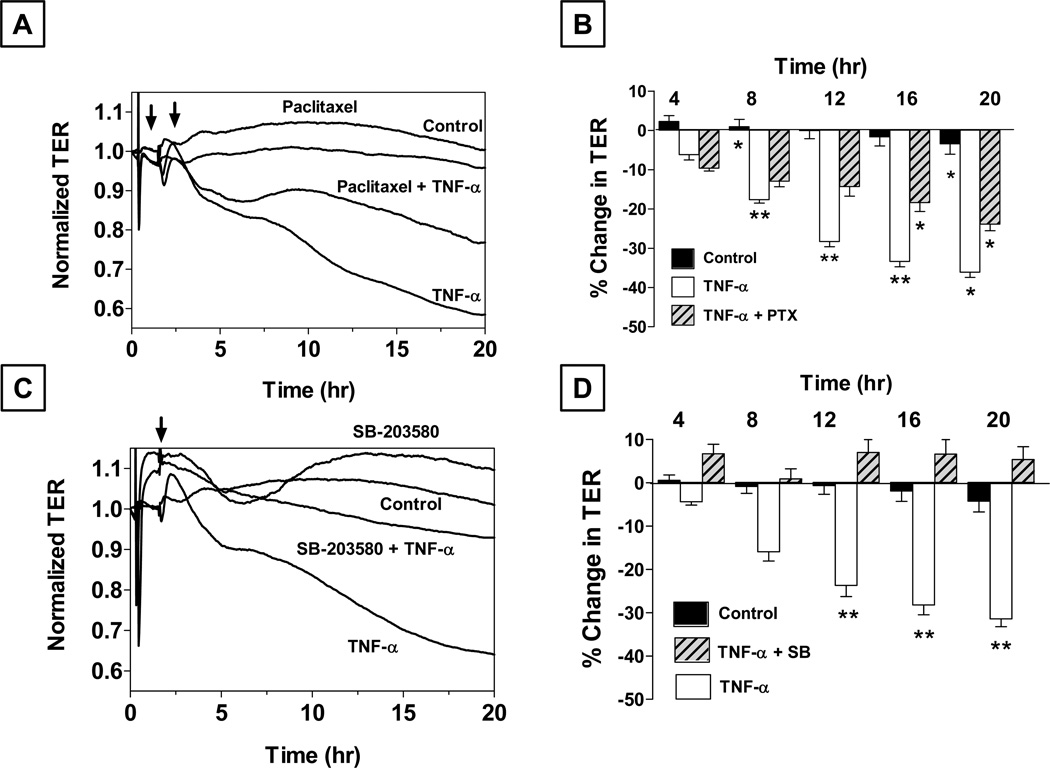
Figure 5. Role of microtubules and p38 MAP kinase in the (TNF-α)-induced response in bovine corneal endothelial monolayers.
Panels A and B: Cells were pretreated with 10 µM paclitaxel (PTX) for 1 hr with or without 20 ng/ml TNF-α Paclitaxel attenuates the decrease in TER by TNF-α. Panel B shows bar graph of experiments similar to that shown in Panel A. The % reduction in TER induced by TNF-α is significantly greater than control beyond 8 hrs. Note: TNF-α + PTX: TNF-α + Paclitaxel. Error bars represent the SEM (n = 6). *Indicates significant difference from the control. C vs. TNF-α: p < 0.001. Paclitaxel significantly opposes (TNF-α)-induced reduction in TER beyond 12 hrs. **Indicates significant difference in TNF-α vs. TNF-α + PTX: p < 0.001. Summarized from our previous publication (Shivanna and Srinivas, 2009). Panels C and D: Pretreatment with SB-203580 (a selective p38 MAP kinase inhibitor; 10 µM) attenuates the decrease in TER by TNF-α. Panel D shows a bar graph of experiments similar to that shown in Panel C. Note: TNF-α + SB: TNF-α + SB-203580. Error bars represent the SEM (n > 5). **Significantly different than TNF-α, p < 0.001. Results summarized from our previous report (Shivanna et al., 2010).