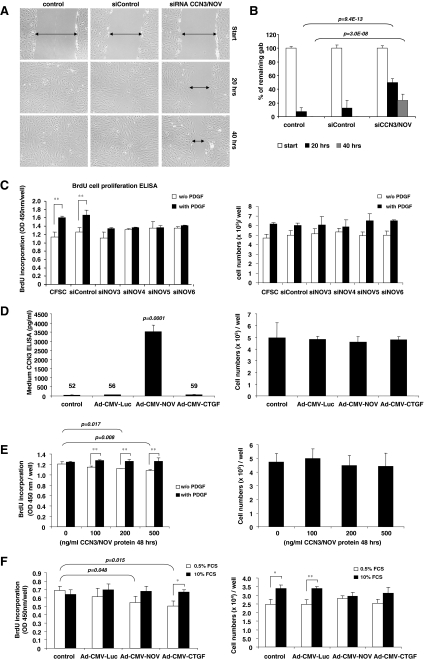
Fig. 6.
CCN3/NOV effects on cell migration and proliferation. a, b Scratch-induced migration assay was performed in CCN3/NOV siRNA-transfected CFSC following a protocol outlined in the Material and Method section. All CCN3/NOV siRNA-transfected CFSC showed a significantly delayed wound gap closing after 20 and 40 h that become visible in light microscopic analysis (a) and was confirmed by gab closing quantification (b). c CFSC were transfected with control siRNA and siRNAs targeting CCN3/NOV. After 24 h starvation, cells were stimulated with PDGF-B in the presence of BrdU. The incorporation of BrdU was measured using an ELISA BrdU colorimetric assay kit. All CCN3/NOV siRNA showed inhibition of PDGF-induced cell proliferation (left panel), but no difference in cell count (right panel). d CFSC were infected with adenoviruses as indicated. Ad5-CMV-rNOV transduction induced high level expression of CCN3/NOV that was effectively secreted into culture medium (left panel), but that no impact on cell count compared to the control culture, control Ad5-CMV-Luciferase and Ad5-CMV-CTGF transduced CFSC (right panel). e CFSC were starved and incubated overnight with indicated doses of exogenous CCN3/NOV, followed by 24 h of 20 ng/ml PDGF-B and BrdU incubation. CCN3/NOV treated cells showed significantly decreased BrdU incorporation at concentrations of 200 and 500 ng/ml in 0.5% FCS (left panel), respectively. However, this analysis revealed no difference in cell numbers (right panel). f Primary HSC were infected with adenovirus as indicated and the medium changed after 24 h to 0.5% or 10% FCS for 48 h or 24 h in the presence of BrdU. Both Ad5-CMV-CTGF and Ad5-CMV-NOV significantly decreased BrdU incorporation in the group of HSC maintained in 0.5% FCS, but no significant difference in 10% FCS (left panel). Cell counts revealed that both Ad5-CMV-CTGF and Ad5-CMV-NOV but not the adenoviral control vector Ad-CMV-Luc attenuate cell growth when cells were cultured in medium containing 10% FCS (right panel)