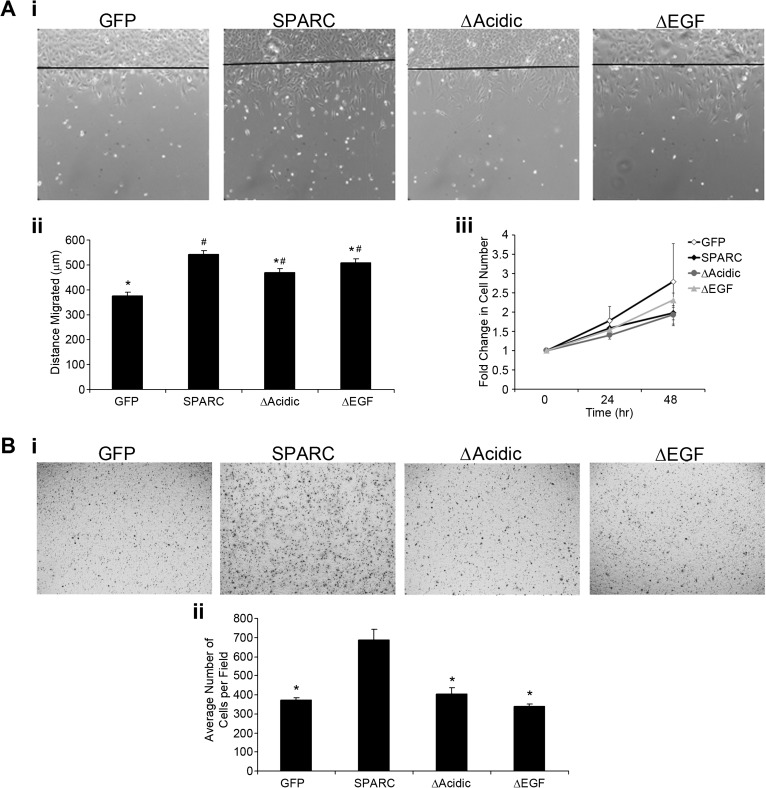
Fig. 5.
Deletion of the acidic domain or the EGF-like module reduces SPARC-induced migration. (A) Wound migration assay. (i) Representative ×10 images of one clone expressing each construct indicate cell migration from the start of the wound after 20 h. (ii) Average distance migrated for both clones expressing each construct. SPARC significantly increased migration over control. Deletion of the acidic domain or the EGF-like module reduced migration compared with SPARC. The deletion mutants migrated farther than control cells. (iii) Fold change in cell number at 24 and 48 h relative to 0 h indicates that increased migration is not due to increased proliferation. (B) Transwell migration assay. (i) Representative ×10 images of one clone expressing each construct indicate migration through transwell filters after 2 h. (ii) Average number of cells per field. Expression of SPARC–GFP increases cell migration compared with control cells. Both deletions reduced migration to control levels. *Significantly less than SPARC (P ≤ 0.033), #Significantly greater than GFP (P < 0.01).