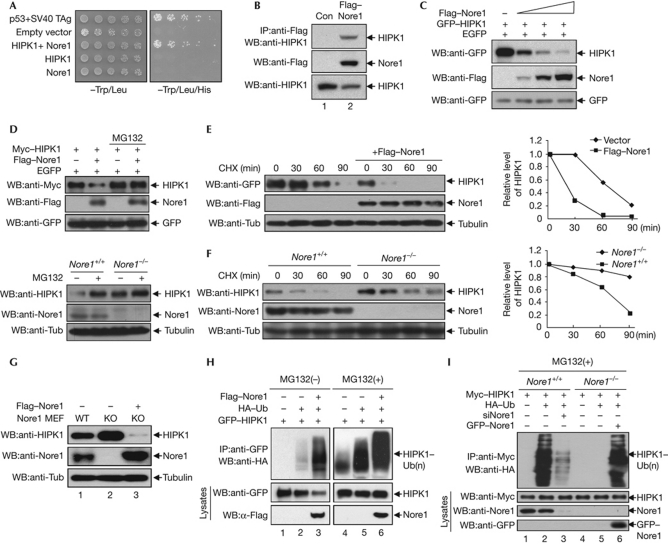
Figure 1.
Nore1-mediated polyubiquitination and degradation of HIPK1 in mammalian cells. (A) The Nore1 (Novel Ras effector 1)-encoding yeast clone and GAL–DBD–HIPK1 plasmid were cotransformed into the yeast AH109 strain. Cells were serially diluted and plated on synthetic dropout plates lacking either Trp/Leu or Trp/Leu/His. (B) HEK293 cells expressing Flag–Nore1 were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Flag antibody, followed by western blotting (WB) using anti-HIPK1 antibody. (C) Increasing amounts of Flag–Nore1 expression plasmids were co-transfected into COS7 cells, followed by western blotting using anti-GFP or anti-Flag antibodies. (D) Myc–HIPK1 plasmids were transfected into COS7 cells in the presence or absence of Flag–Nore1 plasmids, and cells were treated with 5 μM MG132 for 12 h. GFP expression was measured as a transfection control (upper panels). Nore1 wild-type (WT) mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) and Nore1-KO MEFs were treated with MG132 for 12 h, and HIPK1 levels were determined using anti-HIPK1 antibody (lower panels) (E) Analysis of GFP–HIPK1 half-life in the presence or absence of Flag–Nore1. The relative levels of HIPK1 with or without Nore1 expression are quantified on the right panel. (F) HIPK1 levels were increased in Nore1-KO MEF cells compared with wild-type cells, as determined by western blotting using anti-HIPK1 antibody. (G) Introduction of Flag–Nore1 into Nore1-KO MEF cells causes HIPK1 protein levels to decrease. (H) The GFP–HIPK1 expression plasmid was transfected into COS7 cells in combination with HA–ubiquitin and the Flag–Nore1 expression plasmid. Half of the transfected cells were treated with MG132 for 12 h before analysis. (I) Nore1 causes polyubiquitination of HIPK1. Cell lysates were prepared from cells expressing the indicated proteins, and were immunoprecipitated with Myc antibody, followed by western blotting using anti-HA antibody to determine polyubiquitination of HIPK1. CHX, cycloheximide; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HA, haemagglutinin; KO, knockout; Si, short interfering; TAg, T antigen; Tub, tubulin; Ub, ubiquitin.