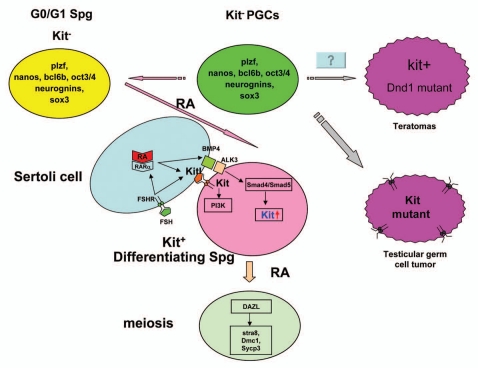
Figure 3.
Summary of Kit/Kitl signaling during spermatogenesis. The c-kit+ PGCs lose c-kit expression and turn into the undifferentiated Spg which characteristically express Plzf, Nanos, Bcl6b, Oct3/4, neurogenin3 and Sox3. Most of those undifferentiated Spg will go into c-kit- mitotic arrest (G0/G1 stage) under control of meiosis-inhibiting factor Cyp26b1. Undifferentiated Spg arrested during mitosis can return to normal spermatogenesis triggered by various differentiation signals. The lack of c-kit negative mitotic arrest disorders will lead to teratomas. RA, FSH and BMP4 may facilitate Spg differentiation as well as the activation of the Kit/Kitl signal pathway. Active RA acts on Sertoli cells through the RARα to stimulate the synthesis of growth factors Kitl, which bind to Kit to activate kit/Kitl/PI3K pathway. ALK3, receptor of BMP4, is specifically expressed in the mitotic Spg during the first week after birth. BMP4 action is mediated by a rapid nuclear translocation of Smad4 and Smad5 which make the Spg start to express c-kit. Mutations of c-kit (resulting in self-activation of Kit) at post-migration stage of Spg will cause bilateral testicular germ cell tumors. Differentiated Spg will go into meiosis after the activation of Kit/Kitl signaling. Dazl is a competence factor for meiosis initiation and germ cells start to express Stra8, Dmc1 and Sycp3 once get into meiosis.