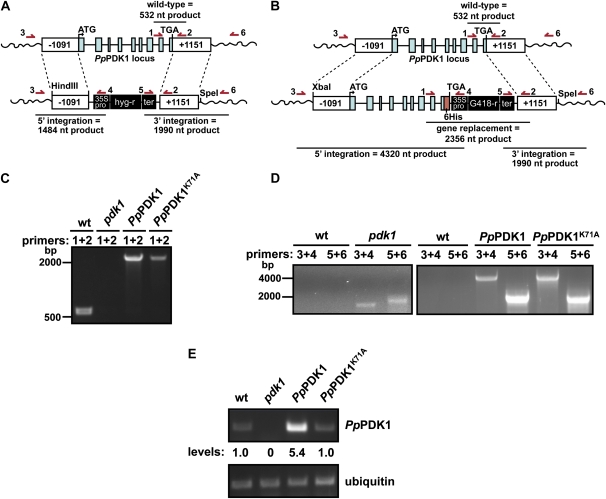
Figure 5.
Production of a pdk1 knockout line and replacement of endogenous PpPDK1 with PpPDK1-6His. A and B, The constructs used to replace the endogenous PpPDK1 locus with a hygromycin marker to create a pdk1 knockout line (A) and to replace the endogenous PpPDK1 locus with PpPDK1-6His or PpPDK1K71A-6His (B). The 6× His tag (maroon box) is not drawn to scale for ease of visibility. Dashed lines indicate regions of homologous recombination. The locations of genotyping primers used in C and D are depicted with arrows above the diagrams. nt, Nucleotides. C, PCR-based genotyping with primers 1 + 2 shows that the indicated P. patens transformants do not contain a wild-type (wt) PpPDK1 gene. D, PCR-based genotyping of the indicated P. patens transformants showing the proper integration of constructs into the endogenous PpPDK1 locus. Wild-type P. patens genomic DNA was used as a negative control for integration of the constructs. E, RT-PCR analysis of gene expression for the indicated genes. Analysis of ubiquitin gene expression was used as an internal control. [See online article for color version of this figure.]