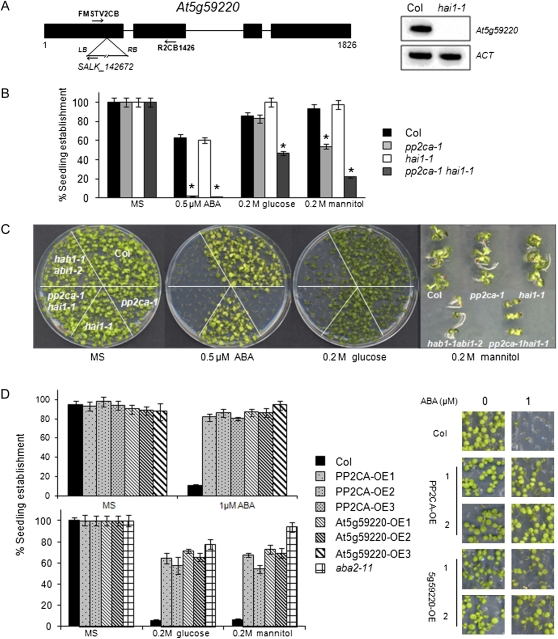
Figure 1.
A, Schematic diagram of the At5g59220 gene showing the position of the T-DNA insertion in the hai1-1 mutant. RT-PCR analysis of mRNAs from wild-type and hai1-1 mutant seedlings is shown. Primers FMSTV2CB and R2CB1426 were used to amplify part of the At5g59220 cDNA. LB, Left border; RB, right border. B, Seedling establishment of the Columbia (Col) wild type, hai1-1, pp2ca-1, and the double mutant in medium supplemented with ABA, mannitol, or Glc. Data show the percentage of seeds that germinated and developed green cotyledons in the different media at 5 d. Values are averages ± se for three independent experiments (200 seeds each). * P < 0.01 (Student’s t test) with respect to the wild type. C, Photograph of a representative experiment taken 10 d after sowing, with a magnification of representative seedlings grown on MS plates supplemented with 0.2 m mannitol. D, Seedling establishment of wild-type, 35S:HA-PP2CA, and 35S:HA-At5g59220 lines in medium supplemented with 1 μm ABA (top panel), 0.2 m Glc, or 0.2 m mannitol (bottom panel). Approximately 200 seeds of each genotype were sown on each plate and scored 4 d later. Photographs were taken after 8 d. OE indicates overexpression lines. [See online article for color version of this figure.]