Scheme 1.
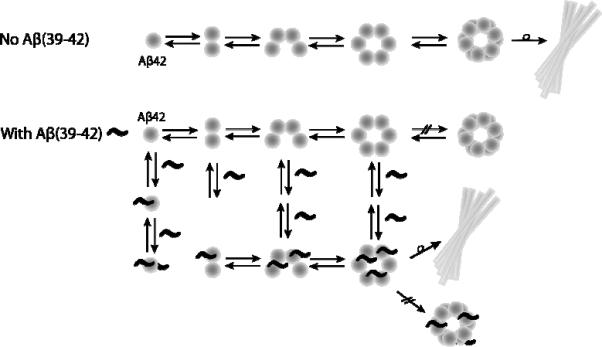
Aggregation mechanism of Aβ42 in the absence or presence of Aβ(39–42), consistent with the results presented here. Normally Aβ42 forms soluble, neurotoxic oligomers before forming larger, fibrillar structures. Aβ(39–42), binds directly to Aβ42 monomer and oligomeric species (n=2 4, 6), and eliminates the formation of large Aβ42 oligomers, driving the formation of non-toxic oligomeric species which also eventually form fibrils.
