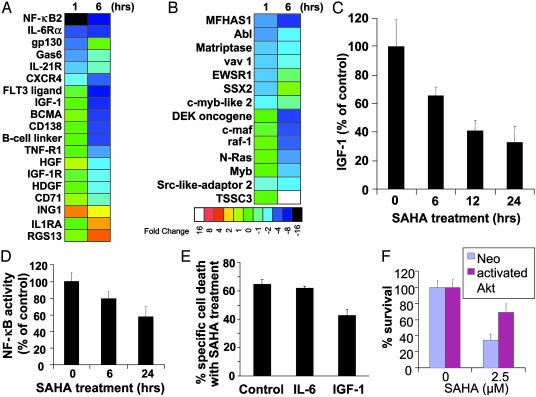
Fig. 2.
Functional clustering analysis of genes implicated in cytokine-induced proliferative/antiapoptotic signaling pathways (A) and oncogenes/tumor suppressor genes (B). SAHA down-regulates signaling pathways for MM cell proliferation and survival, including IGF/IGF-1R and IL-6R/gp130, suppresses expression of multiple oncogenes, and up-regulates several tumor suppressor genes. Color saturation is proportional to magnitude of the difference from the respective control. (C) SAHA treatment (1 μM, 0–24 h) suppresses IGF-1 autocrine production by MM-1S cells. (D) NF-κB DNA binding ELISA confirms that SAHA (1 μM, 0–24 h) suppresses NF-κB activity in MM-1S cells. (E and F) IGF/IGF-1R/Akt pathway protects against apoptosis induced by HDAC inhibition. (E) IGF-1 (200 ng/ml), but not IL-6 (200 ng/ml), reduces the percentage of specific cell death of MM-1S cells after treatment with SAHA (1 μM for 48 h) (MTT survival assay). (F) SAHA-induced cell death (quantified by MTT, mean ± SD) in MM-1S cells transfected with a vector expressing constitutively active Akt or control (neo) vector, after overnight serum starvation, and incubation with or without SAHA for additional 48 h. MM-1S cells transfected with constitutively active Akt construct have reduced sensitivity to SAHA.