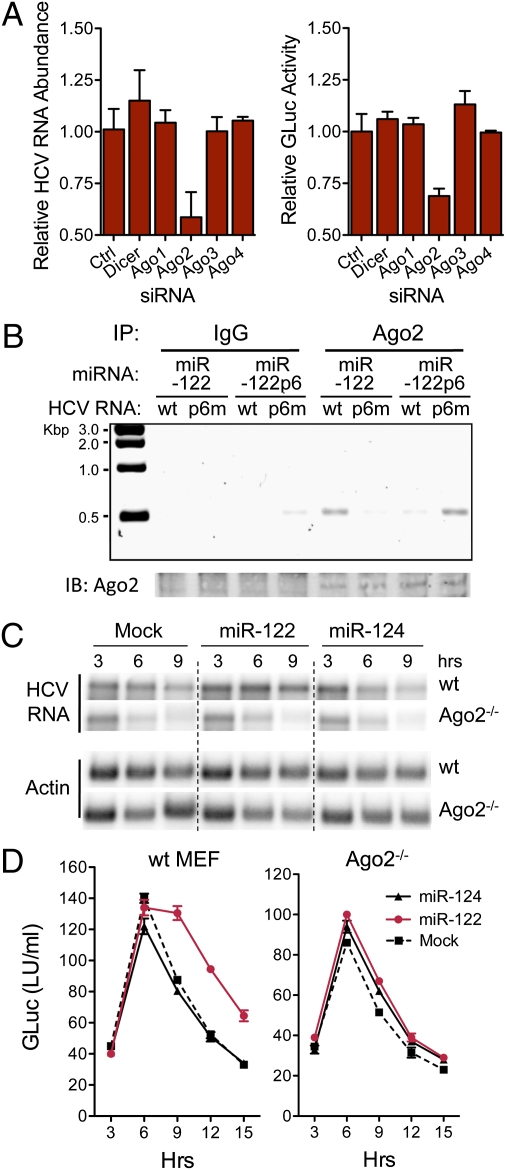
Fig. 4.
Ago2 binds HCV RNA in association with miR-122 and is required for stabilization. (A) RNAi depletion of Ago2 impairs HCV genome amplification in persistently infected (HJ3-5/GLuc2A virus) cells. Left: HCV RNA abundance relative to that in cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA (Ctrl) 72 h after siRNA transfection. RNA was assayed by qRT-PCR; data are mean ± range of paired cultures. Right: GLuc activity secreted into media between 48 and 72 h, relative to si-Ctrl-transfected cultures (mean ± range). (B) miR-122 binds HCV RNA as a complex with Ago2. Lysates were prepared from WT MEFs 6 h after electroporation with HJ3-5/GND or S1-S2-p6m-GND RNA (Fig. 3A), mixed with miR-122 or miR-122p6, and immunoprecipitated with anti-Ago2 antibody. After extensive washing, RNA was extracted from the precipitates and subjected to a one-step HCV-specific RT-PCR (30 cycles). HCV RNA was enriched in precipitates from HJ3-5/GND–transfected cells supplemented with miR-122, or S1-S2-p6m-GND cells supplemented with miR-122p6. (C) Northern blots showing miR-122 does not stabilize HCV RNA in Ago2−/− MEFs. Cells were electroporated with HCV RNA (H77S/GLuc2A-AAG) together with miR-122, miR-124, or no miRNA (Mock), then lysed at 3-h intervals and assayed for HCV RNA abundance. miR-122 stabilized HCV RNA only in WT MEFs and was without effect in Ago2−/− cells. (D) GLuc activity in supernatant fluids from MEFs cotransfected with HCV RNA and the indicated miRNA (mean ± range). Data shown are representative of two or more independent experiments.