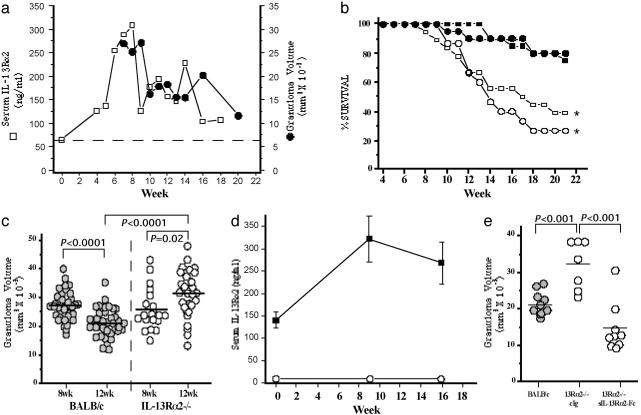
Fig. 1.
IL-13Rα2 down-modulates granulomatous inflammation and prolongs survival in chronic S. mansoni infection. (a) C57BL/6 mice were infected percutaneously with 25–30 cercariae of S. mansoni. Uninfected (“wk 0,” n = 5) and infected mice (n = 5 weekly) were bled from wk 4 to wk 18 postinfection (open squares) to measure serum IL-13Rα2 levels; mean granuloma volumes were also determined (n = 5) from wk 7 to wk 20 (filled circles). The dashed line represents the mean level of serum IL-13Rα2 in naive mice. (b) BALB/c male (filled squares, n = 20), BALB/c female (filled circles, n = 20), IL-13Rα2–/– male (open squares, n = 18), and IL-13Rα2–/– female (open circles, n = 15) mice were infected percutaneously with 25–30 cercariae of S. mansoni. The median survival time for all IL-13Rα2–/– mice after infection was 15 wk (*, P = 0.0002). Survival was analyzed and compared with WT mice by log-rank test using prism 3.0 (GraphPad, San Diego). (c) BALB/c (wk 8, n = 36; wk 12, n = 36) and IL-13Rα2–/– (wk 8, n = 20; wk 12, n = 28) mice were infected and killed on wk 8 and wk 12 postinfection. The circles represent average granuloma measurements for individual mice from three independent experiments. Approximately 30 granulomas were measured in each animal. Relevant statistical comparisons are shown. (d) Uninfected and infected BALB/c(n = 5 per time point, filled squares) and IL-13Rα2–/– (open circles) mice were bled to quantify serum IL-13Rα2 levels at the times indicated. (e) Mice were infected, and liver granuloma size was measured at wk 12 postinfection in the surviving animals: BALB/c mice (n = 9), IL-13Rα2–/– mice treated with control IgG (n = 7), and IL-13Rα2–/– mice treated from wk 6 through wk 12 with 200 μg of soluble IL-13Rα2-Fc (sIL-13Rα2-Fc) (n = 9) injected three times weekly. BALB/c vs. sIL-13Rα2-Fc treated IL-13Rα2–/–, P = 0.011. Other relevant statistical comparisons are shown.