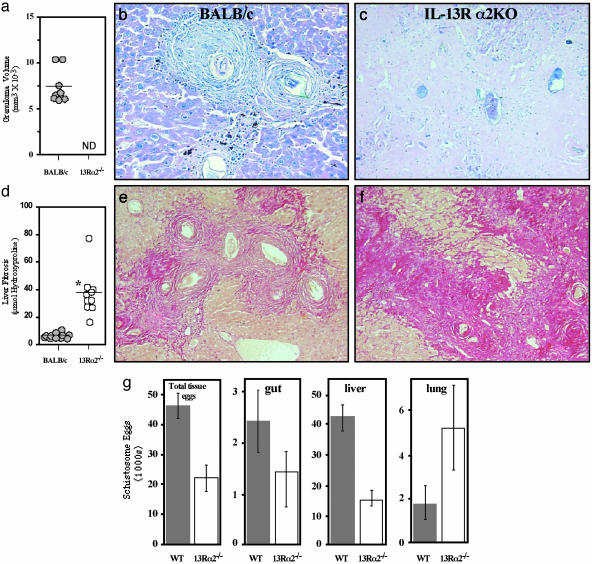
Fig. 2.
Chronically infected IL-13Rα2–/– mice lack viable parasite eggs and newly formed granulomas in the liver and develop significant portal obstruction. BALB/c and IL-13Rα2–/– mice were infected with S. mansoni, and survivors were killed at wk 38 (n ≥ 10 analyzed per group). (a) Liver granuloma size was measured in infected BALB/c mice but could not be determined (ND) in IL-13Rα2–/– mice due to the absence of newly deposited mature eggs. (b) Representative hepatic granuloma from chronically infected BALB/c mice (Giemsa stain). (c) Chronically infected IL-13Rα2–/– mice lack viable parasite eggs in the liver and are devoid of active granulomatous lesions (Giemsa stain). (d) Fibrosis (μmol of hydroxyproline per 1.0 × 104 eggs) is significantly exacerbated in IL-13Rα2–/– mice after 38 wk of infection (*, P < 0.001). (e) Liver sections were prepared from chronically infected (38 wk) BALB/c mice and stained with the collagen-specific stain picrosirius red. Collagen deposition was localized within the granulomas. (f) Liver sections were prepared from chronically infected (38 wk) IL-13Rα2–/– mice and stained with picrosirius red. Large densely staining bands of collagen were seen throughout the liver. (g) Tissues were digested to enumerate egg burdens. The total tissue egg burden per worm pair, total eggs per gut (small and large intestine), and total eggs per liver and lung are shown as averages ± SE.