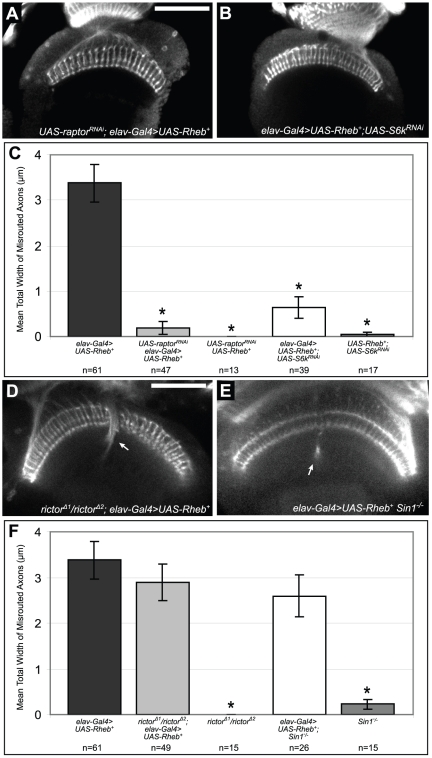
Figure 8. Rheb-mediated axon guidance defects are dependent on TorC1 downstream components, but not on TorC2.
(A–C) Rheb was neuronally expressed in pupal brains along with RNAi constructs against either raptor, a principal component of Tor-complex 1, or S6k, an important downstream mediator of TorC1 activity. Genetic knockdown of either of these critical mediators of TorC1 signaling significantly rescued the axon misrouting defects normally observed in Rheb-overexpressing animals. (D–F) When Rheb was neuronally overexpressed in animals with null mutations in either of the critical TorC2 components rictor or Sin1, we saw no significant rescue of axon guidance defects (arrows). Although Sin1 mutants did show a small degree of axon misrouting even in the absence of Rheb misexpression, this level of defect was not substantial enough to confound the interpretation of our primary results. Asterisks denote a two-tailed Student's t-test statistic of p<0.05 compared to elav-Gal4>UAS-Rheb+ controls. Scale bars are 50 microns.