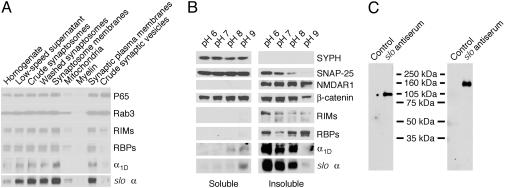
Fig. 3.
Large-conductance KCa channels assemble with β-catenin in the presynaptic active zones of the chicken's brain. (A) Subcellular fractions were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed by Western blotting. In conjunction with other synaptic proteins, the cslo α-subunit is enriched in the fraction containing synaptic plasma membranes (second lane from the right). Note that the crude fraction of synaptic vesicles (right lane) contains little of the cslo α-subunit, whose distribution pattern resembles those of other constituents of the presynaptic active zone, such as RIMs, RBPs, and the Cav channel α1D-subunit. (B) In a solubility analysis of synaptic proteins, synaptosomes were extracted with 1% Triton X-100 at the indicated pH levels; equal volumes of soluble and insoluble materials were then analyzed by immunoblotting. Both the cslo α-subunit and the α1D (Cav1.3) Ca2+-channel subunit were extracted at pH levels >8, a result compatible with their presynaptic localization. β-Catenin is present in both pre- and postsynaptic locations. (C) Brain synaptic proteins were purified on an anti-cslo α-subunit affinity column. The precipitants were then separated by SDS/PAGE, transferred to blots, and detected with antiserum directed against either anti-β-catenin (Left) or anti-slo α-subunit (Right). The result indicates that β-catenin and the slo α-subunit associate in a protein complex.