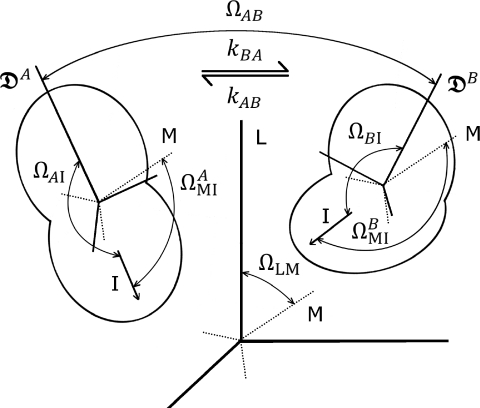
Figure 1.
Schematic of a molecular system undergoing inter-conversion between two conformations A and B with rate constants kBA and kAB for the forward and backward processes, respectively. L denotes a laboratory-fixed reference frame, M a reference frame rotating with diffusional tumbling, and I the frame of a vector of interest giving rise to an observable signal. ΩLM specifies the orientation of the tumbling molecular frame relative to the laboratory-fixed frame. denotes the diffusion tensor of conformation ε, while ΩεI specifies the orientation of the vector of interest relative to the associated principal axes, and ΩAB specifies the rotation required to transform between the principal axis frames of states A and B. The orientation of the vector of interest in state ε relative to the molecular frame is given by . Note that the resulting vector autocorrelation function depends only on , ΩAB, ΩεI, and the rate constants for inter-conversion between the states.