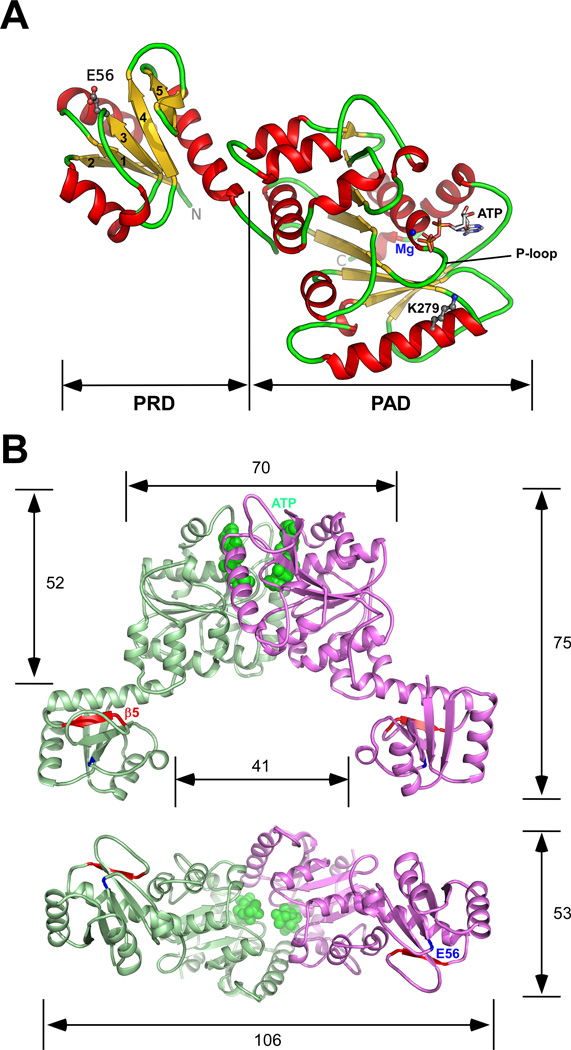
Fig. 2.
The crystal structure of TadZ from E. rectale (ErTadZ). (A) The monomer of ErTadZ consists of two domains: the atypical receiver domain (ARD) and the atypical ATPase domain (AAD). Glu56 and Lys279 are shown as ball-and-sticks; ATP is shown as sticks, and Mg2+ as a blue sphere. (B) ErTadZ dimer and molecular dimensions (in Å) with ATP in green spheres. Glu56 and strand β5, corresponding to the canonical phosphorylation site and output surface of a canonical RD, are highlighted in blue and red respectively.