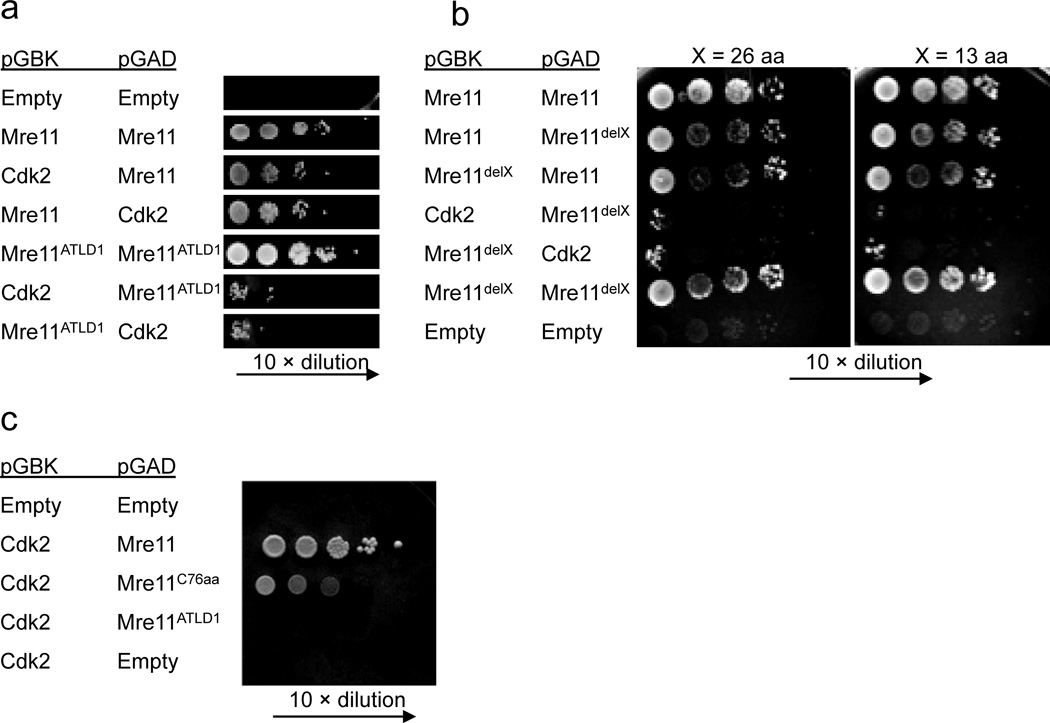
Figure 4. Direct interaction between Mre11 and CDK2.
(a–c) Yeast two hybrid analyses using pGBK (bait) and pGAD (prey) plasmids expressing the genes indicated (left). Mre11 dimerization is positive control. Empty vectors are negative control.
(a) Mre11 and CDK2 interact. The interaction requires the C-terminal 78 amino acids of Mre11 missing in Mre11ATLD1.
(b) Mre11–CDK2 interaction requires the very C-terminus of Mre11. delX (left) indicates deletion of 13 or 26 amino acids (top) from the Mre11 C–terminus.
(c) The C-terminus of Mre11 is sufficient for interaction with CDK2. C76aa indicates expression of the final 76 amino acids of Mre11.