Figure 1.
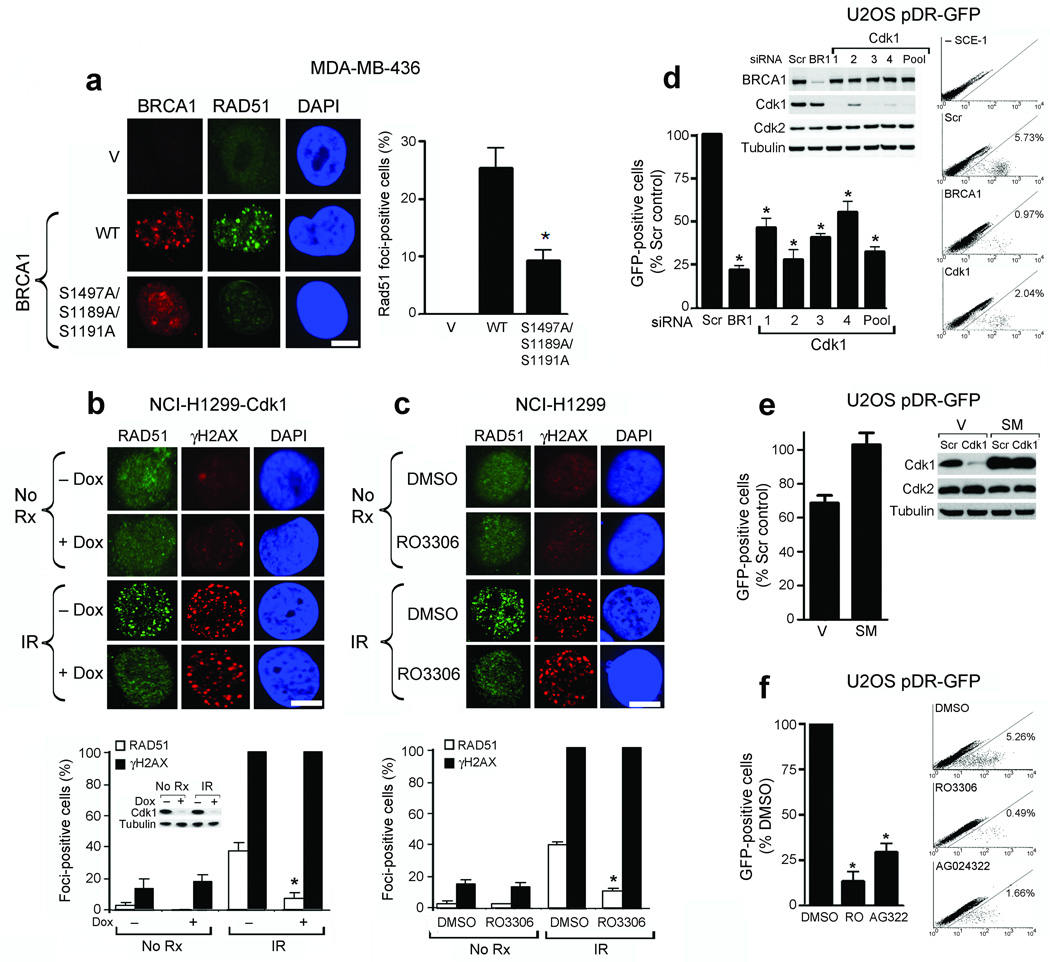
Cdk1 depletion or inhibition reduces Rad51 focus formation and HR. (a) Detection of BRCA1, Rad51 and DAPI by immunofluorescence after IR in empty vector (V), wild-type (WT) or S1189A/S1191A/S1497A mutant HA-tagged BRCA1-expressing MDA-MB-436 cells. (Left) Representative foci-containing cells; (Right) Mean number of BRCA1- expressing cells with ≥ five Rad51 foci ± standard error (SE) over three experiments. (b) Detection of Rad51, γ-H2AX and DAPI by immunofluorescence in NCI-H1299 cells inducibly expressing shRNA targeting cdk1, untreated or treated with IR ± doxycycline. Western blots demonstrate cdk1 knockdown. (c) NCI-H1299 cells, untreated or treated with IR with DMSO or RO-3306 and stained as in (b). For (b and c): (Upper Panels) Representative foci-containing cells. (Lower Panels) Mean number of cells containing ≥ five Rad51 and γ-H2AX foci ± SE over three experiments. (d) Detection and quantification of GFP-positive U2OS pDR-GFP cells after treatment with scrambled siRNA (Scr), or siRNAs targeting BRCA1 (BR1) or cdk1 (1–4 individual siRNAs and 1–4 pooled). Western blots demonstrate cdk1 knockdown. (e) Quantification of GFP-positive U2OS pDR-GFP cells expressing empty vector (V) or cdk1 containing a silent mutation (SM) after treatment with scrambled siRNA (Scr) or cdk1 siRNA. Western blots demonstrate protein knockdown. (f) Detection and quantification of GFP-positive U2OS pDR-GFP cells after treatment with DMSO, RO-3306 or AG024322. For (d–f), mean ± SE number of GFP-positive cells is expressed as a percentage of scrambled siRNA or DMSO-treated controls over three experiments. *’s indicate statistically significant P values. Scale bars, 10 µM.