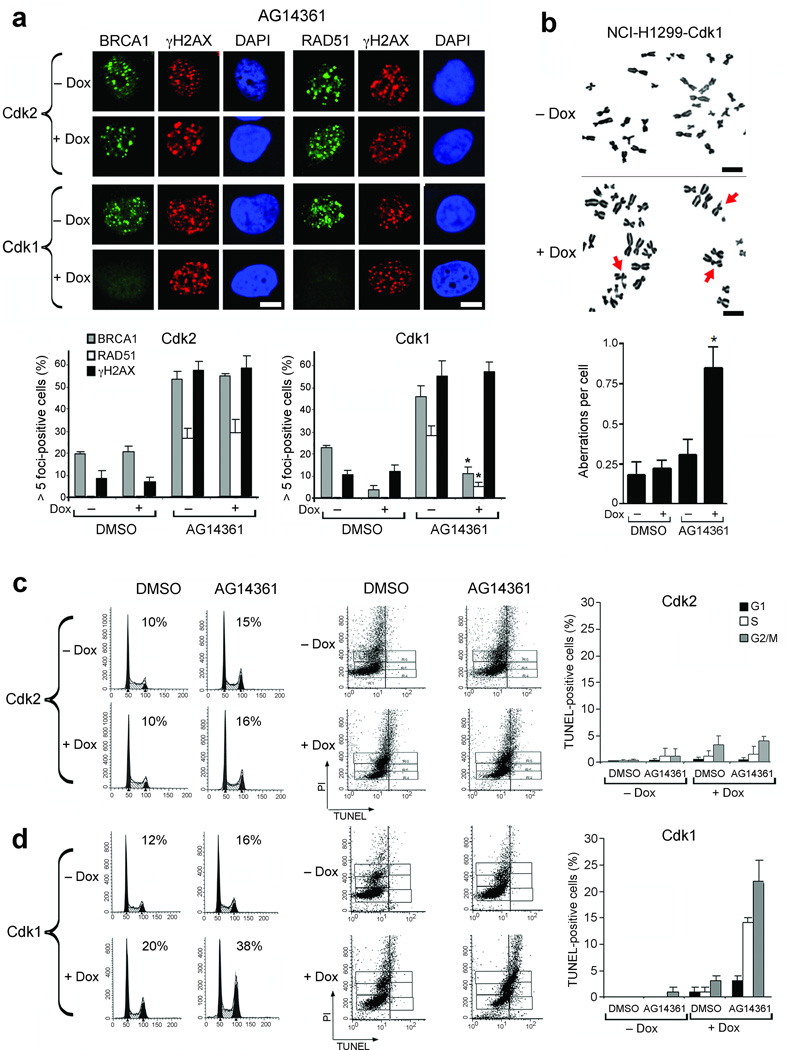
Figure 2.
Cdk1 depletion results in reduced Rad51 foci, multiple chromosome aberrations, G2/M accumulation and cell death following PARP inhibition. (a) Detection of BRCA1, Rad51, γ-H2AX and DAPI by immunofluorescence in NCI-H1299 cells inducibly expressing shRNA targeting cdk2 or cdk1 treated with AG14361 ± doxycycline. (Upper Panels) Representative foci-containing cells. (Lower Panels) Mean number of cells containing ≥ foci ± SE over three experiments. (b) Metaphase spread analyses of NCI-H1299-cdk1 cells analyzed for chromosomal breaks after 24 hours treatment with AG14361. (Upper panels) Representative metaphase spreads; chromosomal aberrations are indicated by arrows. (Lower panels) mean number of chromosome aberrations per cell, ± SE over three experiments. For (a and b), *’s indicate statistically significant P values. (c) Cell cycle profiles (left) and detection of TUNEL-positive (middle) NCI-H1299-cdk2 cells treated with DMSO or AG14361 ± doxycycline. Vertical lines indicate the TUNEL-positive threshold. (Right) Mean percent of TUNEL-positive cells in G1, S and G2/M ± SE over three experiments. (d) NCI-H1299-cdk1 cells treated and analyzed as in (c). Scale bars, 10 µM.