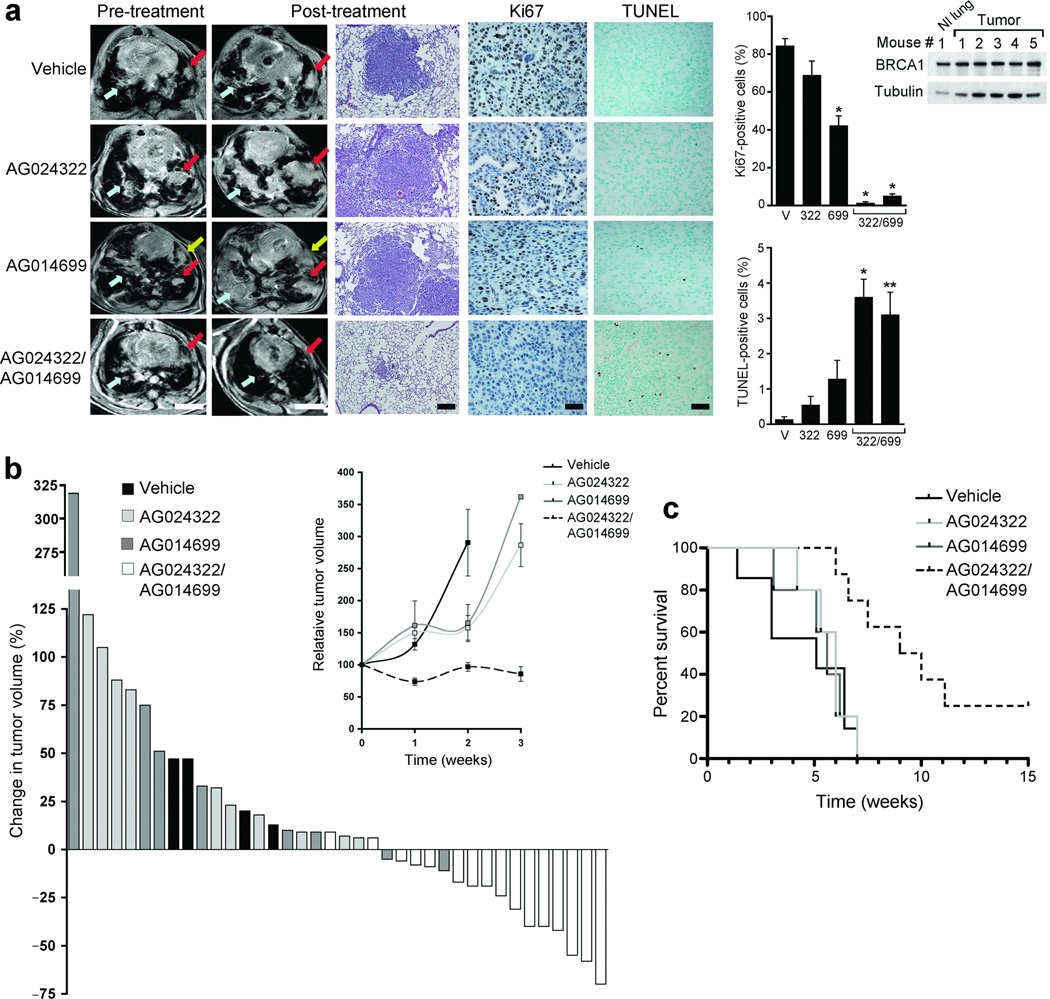
Figure 6.
Combined inhibition of cdk1 and PARP causes tumor regression and prolongs survival in the KrasG12D p53L/L mutant lung cancer mouse model. (a) (Left) Representative MRI images of lung tumor volumes before and after one week of the indicated treatments. Colored arrows show matched lesions in the pre- and post-treatment images; scale bars, 4.5 mm. (Middle) Representative H and E stains (scale bars, 500 µM), as well as Ki67 and TUNEL staining of tumors after the indicated treatments (scale bars, 100 µM). Graphs show the mean ± SE number of positive cells; results for two mice treated with both AG024322 and AG014699 are shown. *, P ≤ 0.0002; **, P < 0.002 of treatment compared to vehicle. (Right) Western blot demonstrates BRCA1 expression in mouse normal lung or tumor tissue. (b) Waterfall plot showing percent change in tumor volume after 1 week of treatment measured by MRI compared to start of treatment for each mouse. (Inset) Mean relative tumor volume ± SE over the first 3 weeks of treatment for mice treated as indicated. At 1 and 3 weeks, each data point represents the average of 4–16 mice; at 2 weeks, 2–4 mice in each group were analyzed. At 3 weeks, the SE for mice treated with AG014699 was ± 171.2, based on one tumor that was increased by > 900-fold. (c) Kaplan-Meier analyses demonstrating median survival times from the start of treatment of mice treated with vehicle, AG024322, AG014699 or both of 5.1, 6, 5.6 and 9.5 weeks, respectively.