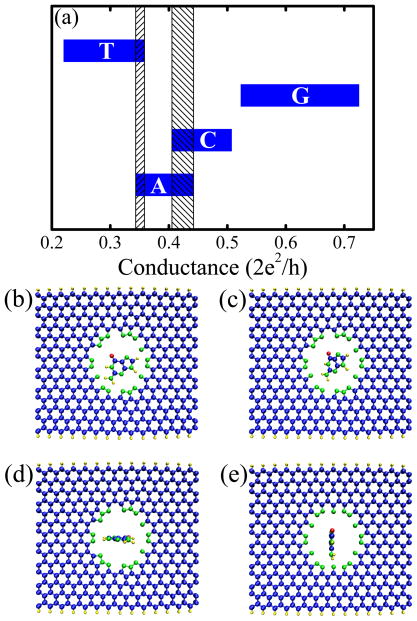
Figure 3.
(a) The variation of the room-temperature conductance of 14-ZGNR with N-pore due to the rotation of A, C, G, T nucleobases within the nanopore. The shaded vertical rectangles mark the regions of overlap between the conductance intervals associated with different nucleobases. The specific positions of a nucleobase (guanine in the example) within the N-pore that define the conductance intervals shown in panel (a) are illustrated in [see coordinate system in Figure 1]: (b) nucleobase within the xy-plane (hosting also ZGNR and nanopore); (c) nucleobase within the plane inclined at an angle of 45° with respect to the xy-plane; (d) nucleobase within the xz-plane; (e) nucleobase within the yz-plane. The conductances in panel (a) were computed using our homegrown MT-NEGF-DFT code.19,20