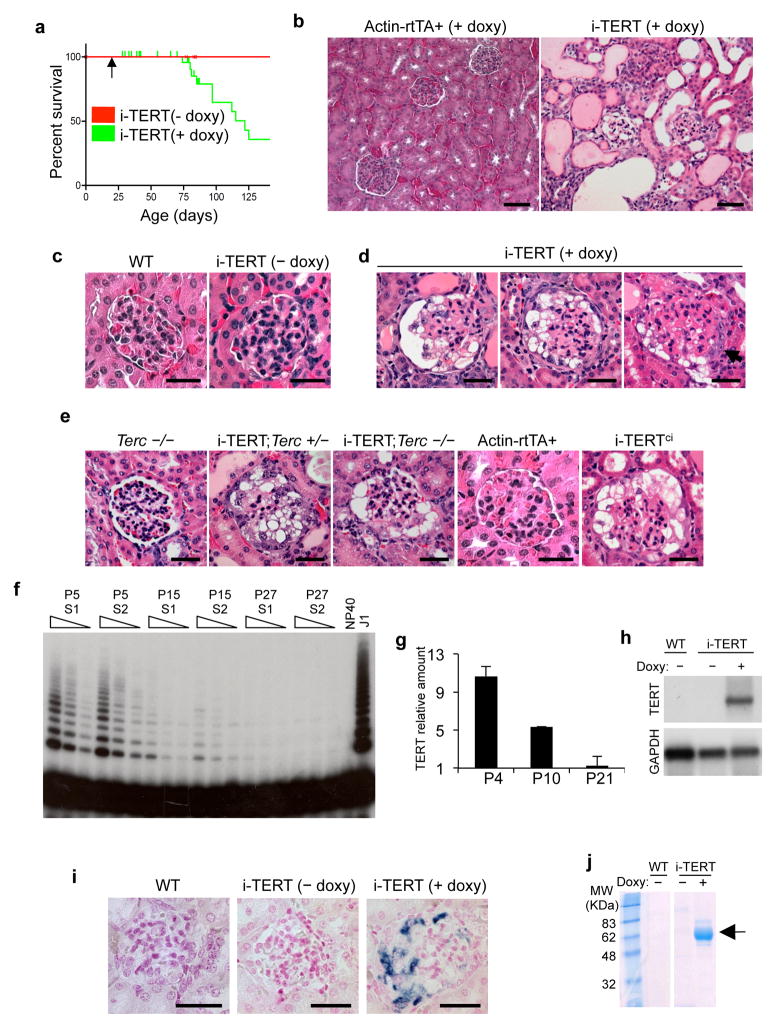
Figure 1.
Conditional induction of TERT impairs survival and induces a collapsing glomerulopathy. (a) Survival of i-TERT mice (− doxy, red; + doxy, green). Doxycycline (doxy) initiated at age 21 days (arrow). P<0.001 by Logrank test. (b) Kidney histology from Actin-rtTA+and i-TERT mice each on doxy for 44 days. H&E, scale bar = 50 μm. (c–e) Glomerular histology from: (c) wild-type mice (left panel) and i-TERT mice off doxy (right panel); (d) i-TERT mice on doxy for 44 days; (e) Terc−/−, i-TERT;Terc+/− and i-TERT;Terc−/− mice on doxy for 56 days, and Actin-rtTA+ and i-TERTci mice each on doxy for 30 days. H&E, scale bar = 25 μm. (f) Telomerase activity by TRAP in wild-type whole mouse kidney at day 5 (P5), day 15 (P15), and day 27 (P27) after birth. Two mice analyzed for each time point (S1 and S2). Range of concentrations represents two-fold serial dilutions of extract. Lysis buffer (NP40), negative control; mouse ES cells (J1), positive control. (g) TERT mRNA levels by qRT-PCR in whole mouse kidney at 4, 10, and 21 days of age. (h) Northern blot analysis for TERT mRNA in kidney from wild-type and i-TERT mice off (−) or on (+) doxy. (i) RNA in situ hybridization for TERT mRNA in wild-type and i-TERT mice off (−) or on (+) doxy. Scale bar = 25 μm. (j) Analysis of protein in urine by SDS-PAGE from wild-type (WT) or i-TERT mice off (−) or on (+) doxy.