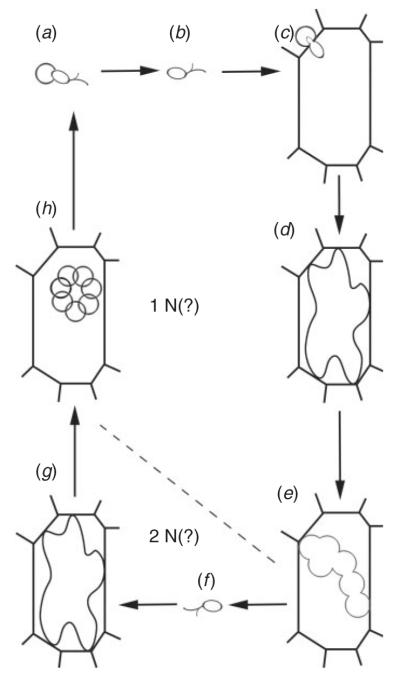
Fig. 2.
Generalised phytomyxean life cycle. Not all stages have yet been reported for some phytomyxean species, and the life cycle may be complicated in some species. (a) Release of primary zoospores from resting spores. (b) Free primary zoospore. (c) Infection of a suitable host. (d) Primary plasmodium inside a host cell. (e) Lobed zoosporangia. (f) Secondary zoospore. (g) Secondary plasmodium formed after infection of a suitable host with at secondary zoospore. (h) Resting spores.