Figure 5. Impaired WRN relocalisation in nuclear foci and association with 9.1.1 complex in cells expressing a WRN mutant bearing a deletion in the RAD1-bindign region.
(A) Western blotting on extracts from WS cells stably expressing the Flag-tagged wild-type WRN (WRNwt) or the 112-121 deletion mutant (WRNdel) showing levels of WRN using an anti-WRN antibody. WS cells were used as a negative control and tubulin as loading control.
(B) Analysis of the association with 9.1.1 of the WRN mutant protein with deletion in the 9.1.1-binding region. Five μg of wild-type or 112-121 deletion mutant GST-tagged N-terminal fragment of WRN (1-550) was purified from E. coli and incubated with 2μg of HeLa nuclear extracts. After release in sample buffer and separation on SDS-PAGE, the presence of RAD1 in the pull-down material was assessed by immunoblotting using an anti-RAD1 antibody. One-tenth of the released material was subjected to immunoblotting using an anti-GST antibody to visualize the amount of GST-NWRN fragments. Pull-down using uncoupled GST-binding beads was used as negative control.
(C) Analysis of WRN relocalisation to nuclear foci after replication arrest. Images show WRN nuclear distribution with or without an 8h HU treatment. The inset shows the percentage of WRN positive nuclei. Data are presented as means of three independent experiments+/− standard errors.
(D) Analysis of WRN-9.1.1 association in cells expressing WRNdel. 293T cells transiently expressing the Flag-tagged WRNwt or the Flag-tagged WRNdel protein were treated with 2mM HU for 8h prior to lysis and immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag antibody. The presence of RAD9 and RAD1 were assessed by immunoblotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies. Immunoprecipitation using normal IgG was used as a negative control. Inputs contained 15% of the total lysates used for immunoprecipitation. A fraction of the lysate (1/50) was also analysed by immunoblotting to evaluate the amount of the wild-type and mutant form of WRN expressed in 293T cells. RAD9 immunoblotting was used to confirm the presence of RAD9 in the lysates and as loading control.
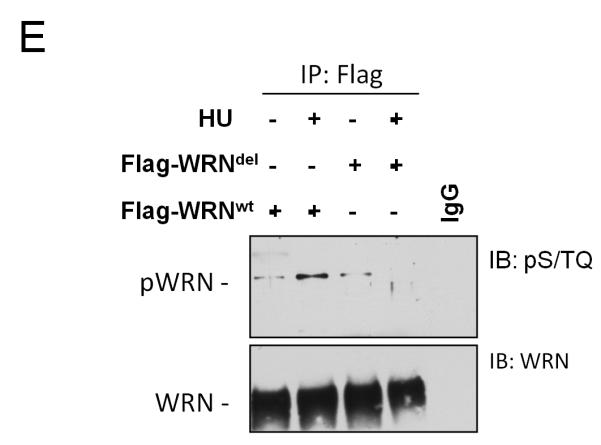
(E) Analysis of WRN phosphorylation at S/TQ sites in the 112-121 deletion WRN mutant after HU treatment. Cells expressing the wild-type and the WRNdel mutant were treated with 2mM HU for 6h prior to lysis and immunoprecipitation using an anti-Flag antibody. WRN phosphorylation was evaluated by immunoblotting in the WRN immunoprecipitates with an anti-pST/Q antibody (IB: pS/TQ). The total amount of the immunoprecipitated WRN protein was determined by anti-WRN immunobloting (IB: WRN). Immunoprecipitation using normal mouse IgG (IgG) was used as a negative control.

