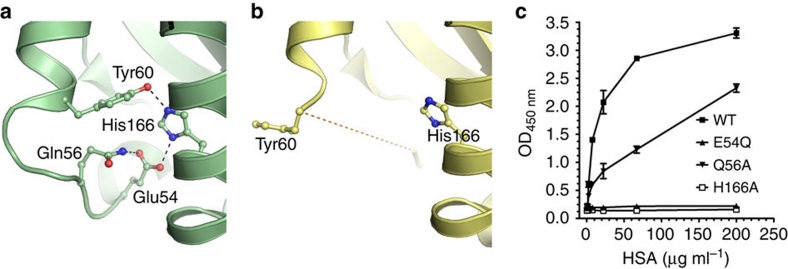
Figure 4. His-166 of hFcRn stabilizes a flexible loop in a pH-dependent manner.
Close-up view of the FcRn HC loop area at different pH conditions. (a) At low pH (4.2), the positively charged His-166 forms charge-stabilized hydrogen-bond interactions with Glu-54 and Tyr-60 within the surface-exposed loop in hFcRn23. (b) At high pH (8.2), the uncharged His-166 looses the interactions with Glu-54 and Tyr-60, and the loop between residues Trp-51 and Tyr-60 becomes flexible and structurally disordered (represented by the dashed line)8. (c) Binding of 0.5 μg ml−1 of hFcRn WT and mutants (E54Q, Q56A and H166A) to titrated amount of HSA (0.3–200 μg ml−1) coated in ELISA wells at pH 6.0. n=4. All data are presented as mean±s.d.