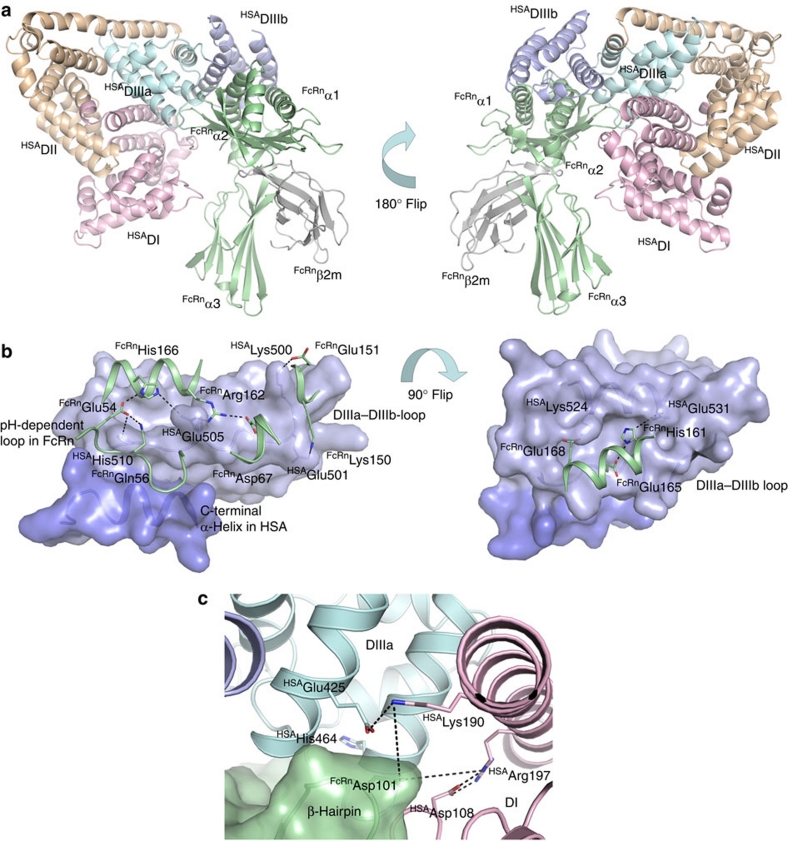
Figure 5. A proposed hFcRn-HSA docking model.
(a) An overview of the docked molecules in two orientations showing the FcRn HC (green), β2m (grey) and the three HSA α-helical domains DI (pink), DII (orange) and DIII (cyan/blue). The HSA DIII is split into DIIIa (cyan) and DIIIb (blue). (b) Close-up view of the interaction interface between hFcRn (green cartoon) and HSA (blue surface) in the docking model. The C-terminal end of HSA (dark blue) and the loop corresponding to residues 490–510 between subdomains DIIIa and DIIIb form a crevice on the HSA surface into which the pH-dependent and flexible loop in hFcRn (residues 51–59) might bind. His-166 of hFcRn may form strong, charge-stabilized interactions with HSA residues Glu-54 and Glu-505. HSA Glu-505 could further interact with hFcRn Arg-162. Possible salt-bridges are formed between Lys-150 and Glu-151 of hFcRn with Glu-501 and Lys-500 of HSA. A cleft on the HSA surface is formed between the loop connecting DIIIa and DIIIb and the α-helix encompassing residues 520–535. His-161 of hFcRn may interact with Glu-531 of HSA at low pH, and the complex could be further reinforced by the salt-bridge between hFcRn Glu-168 and HSA Lys-524. (c) Interaction interface between hFcRn (green surface) and HSA (pink, blue and cyan cartoon) in the docking model. A β-hairpin loop in hFcRn is wedged in-between domains DI (pink) and DIIIa (cyan) in HSA. The hFcRn Asp-110 could be a partner to either Lys-190 or Arg-197 of HSA following some structural rearrangements in this interface. The conserved His-464 is located in the DIIIa α-helix contacting the β-hairpin loop.