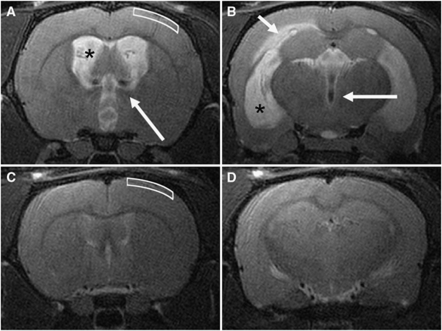
Figure 2.
Representative T2-weighted coronal magnetic resonance images at the level of the foramen of Monro (A, C) and the temporal horn of the lateral ventricles (B, D). In the acute communicating hydrocephalus (CH) rat (A, B), the lateral ventricles (asterisks) and third ventricle were markedly dilated. In some animals, the periventricular white matter was edematous (short arrow), and flow voids due to elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pulsatility were usually noticeable (long arrows). This pattern was also observed in chronic CH animals (not shown). In a control rat (C, D) the lateral ventricles were slitlike and no edema was found in the periventricular white matter. The white boxes (A, C) show the region of the cortex imaged by microscopy, to a depth of ∼500 μm from the pial surface, primarily covering cortical layers 2 and 3 (the dorsal edge of layer 4 lies at ∼500 μm in a control animal).