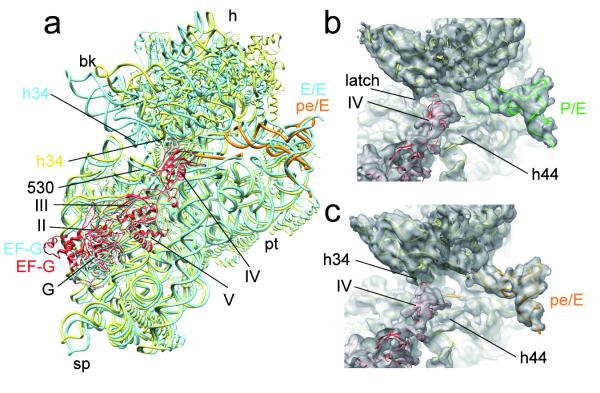
Fig. 3. EF-G stabilizes the swiveled head movement in the TIPOST state.
a, Comparison of the position of FA-stalled EF-G and the 30S subunit between TIPOST and the POST state 70S•EF-G•GDP•FA19. All shown components of the POST state 70S•EF-G•GDP•FA19 are depicted as blue ribbons. The 30S, EF-G and pe/E-tRNA of the TIPOST are represented by yellow, red and orange ribbons, respectively. b, c, Close-up on the decoding region and domain IV of EF-G in the same orientation as in (a). The surfaces of TIPRE (b) and TIPOST (c) are transparent with molecular models in ribbons representation (30S subunit, yellow; EF-G, red, P/E-tRNA, green and pe/E-tRNA, orange). The arrows mark the closed latch between h34 and the 530 region of TIPRE (b) and the interaction between h34 and domain IV of EF-G within TIPOST.