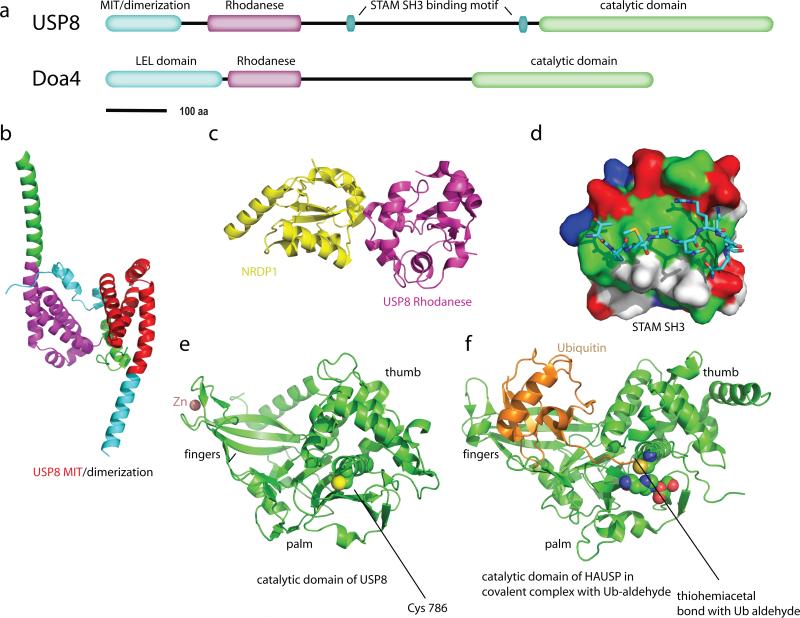
Figure 6.
The Cys isopeptideases USP8 and Doa4. (a) Domain architecture of USP8 and Doa4. (b) Dimeric structure of the N-terminal domain of USP8 (2A9U). The portions of the two monomers the correspond to the MIT sequence motif are colored red and magenta, and the remainder of the subunits are colored green and cyan, respectively. (c) Structure of the rhodanese domain of USP8 (2GWF; magenta) in complex with the non-catalytic C-terminal domain of the ubiquitin ligase NRDP1 (yellow). (d) A surface representation of the SH3 domain of STAM2 (1UJ0), colored green (hydrophobic residues), blue(basic residues), red (acidic residues), and white (uncharged polar residues). USP8 residues 699-709 are shown in a stick model colored by atom type. (e) Catalytic domain of USP8 in an inactive conformation (2GF0). The non-catalytic (structural) zinc ion is colored salmon. (f) Catalytic domain of HAUSP in covalent complex with Ub-aldehyde (1NBF), as a model for the active form of USP8. The residues of the Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad are shown in space filling spheres and colored by atom type.