Fig 1.
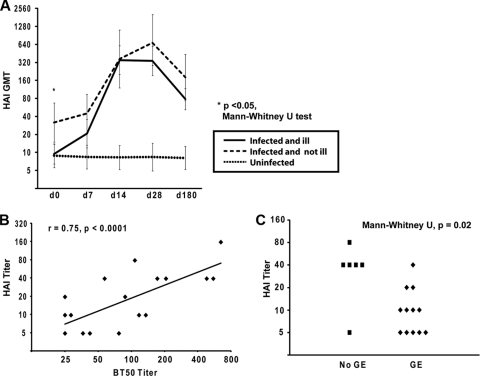
(A) Kinetics of Norwalk virus-specific antibody by hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) assay. Infected, asymptomatic individuals (n = 6) had a higher baseline geometric mean titer (GMT) than infected individuals who developed gastroenteritis (n = 12). Uninfected individuals did not demonstrate a rise in HAI GMT (n = 16). Data are presented with 95% confidence intervals of the GMT. (B) Among infected persons (n = 18), the HAI titer correlated with the blocking antibody titer at the baseline (Pearson's correlation). BT50, the level of antibody that blocks 50% of the signal generated from binding of Norwalk virus VLPs to HBGAs in vitro. (C) Among infected persons, baseline HAI titer is associated with clinical outcome. GE, gastroenteritis.