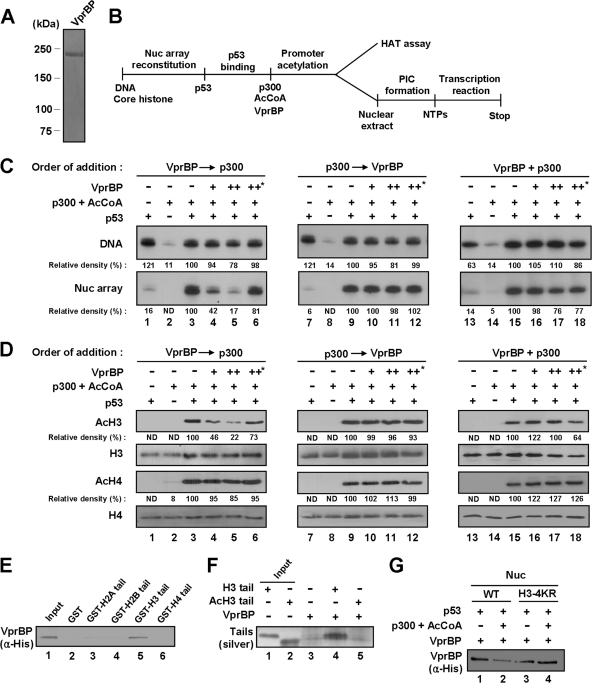
Fig 2.
VprBP-mediated repression of chromatin transcription and H3 acetylation. (A) Analysis of purified VprBP by 8% SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (B) Outline of chromatin HAT and transcription assays. Abbreviations: AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; PIC, preinitiation complex; NTPs, nucleotide triphosphates. (C) Repressive effect of VprBP on chromatin transcription. p53ML-601 nucleosome array or histone-free p53ML-601 DNA was transcribed in the presence of p53, p300, Ac-CoA, and/or VprBP as summarized for panel B. Prior to transcription, p300 and VprBP were added together or sequentially as indicated. Heat-inactivated VprBP was used in control transcription reactions, marked by an asterisk (lanes 6, 12, and 18). Data were quantitated by using a phosphorimager, and the results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Repressive effect of VprBP on H3 acetylation. The p53ML-601 nucleosome array was incubated with p53, p300, Ac-CoA, and/or VprBP as summarized in panel B. Acetylation of nucleosome arrays was detected by Western blotting with anti-acetyl H3 and H4 antibodies (AcH3 and AcH4). Western blot analyses of H3 and H4 confirmed equal loading of histones (H3 and H4). (E) Selective interaction of VprBP with H3 N-terminal tail. His-tagged VprBP was tested for binding to GST (lane 2) or GST-histone tail fusion (lanes 3 to 6) proteins. VprBP binding to histone tails was determined by Western blot analysis using anti-His antibody. Lane 1 represents 10% of VprBP used in the binding reactions. (F) Selective interaction of VprBP with unmodified H3 tail. Unmodified (H3) and acetylated (AcH3) H3 peptides (amino acids 1 to 28) were synthesized and incubated with His-tagged VprBP immobilized on Ni-NTA agarose beads. After extensive washing, bound H3 peptides were resolved in a 4 to 20% SDS-PAGE gel and silver stained. Input lanes 1 and 2 represent 10% of tail peptides used in the binding reactions. (G) Preferential binding of VprBP to unmodified nucleosome. Nucleosomes containing wild-type or mutant H3 were reconstituted on biotinylated 207-bp p53 RE and incubated with p300, p53, and/or Ac-CoA. After reconstituted nucleosomes and free DNA were immobilized on streptavidin-agarose beads, the interaction assays were performed with VprBP. The presence of VprBP in the beads was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-His antibody.