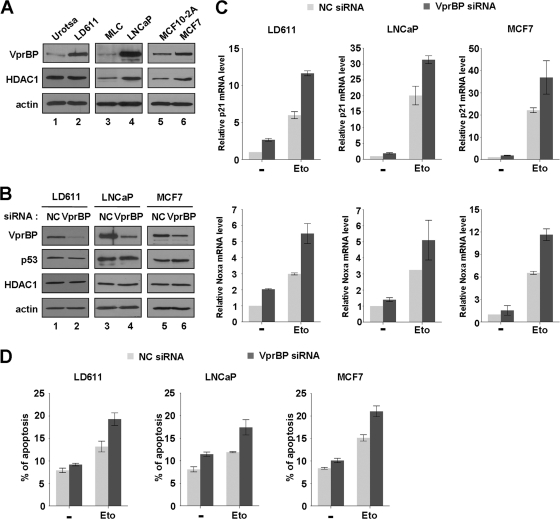
Fig 7.
Stimulation of p53 transcription and apoptosis by VprBP knockdown. (A) Western blot analysis of normal and cancer cells. Exponentially growing normal (Urotsa, MLC, and MCF10-2A) and cancer (LD611, LNCaP, and MCF7) cells were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-VprBP, anti-p53, and anti-HDAC1 antibodies. Actin served as a control for equal protein loading. (B) RNAi-mediated depletion of VprBP. LD611, LNCaP, and MCF7 cells were transfected with a control siRNA (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or a siRNA directed against VprBP (lanes 2, 4, and 6) for 72 h and analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. All analyses were performed in parallel for each of the three cell lines. (C) Activation of the p21 and Noxa genes by VprBP depletion. Cells were first transfected with siRNA targeting VprBP or an irrelevant control (NC) as in panel B and treated with or without etoposide (100 μM) for 24 h. Transcription levels of the p21 and Noxa genes were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (D) Upregulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis by VprBP depletion. After transfected with either a control siRNA or a VprBP siRNA, cells were DMSO treated or etoposide treated as for panel C. The apoptotic status of cells was analyzed by assessing annexin V-FITC fluorescent intensity. Averages and standard deviations are shown for data from three independent experiments.