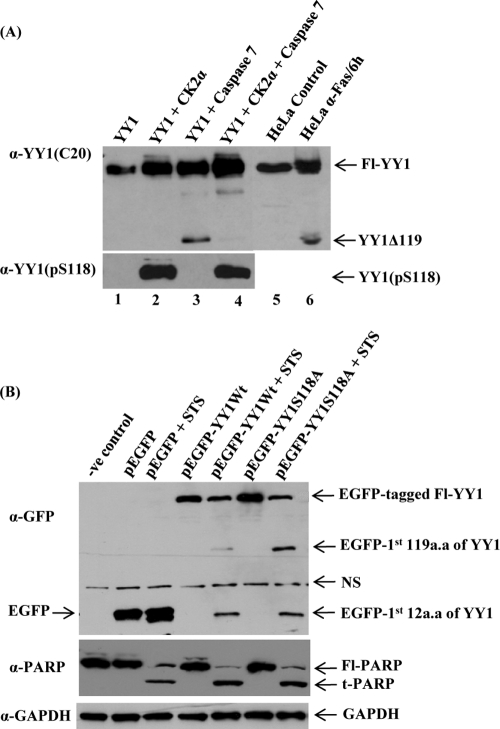
Fig 5.
Phosphorylation of YY1 at S118 decreases its susceptibility to cleavage by caspase 7. (A) Bacterially expressed and purified YY1 was incubated with nonradioactive cold ATP in kinase buffer in the presence or absence of purified CK2α. The kinase reaction mixtures were then used as substrate sources for an in vitro cleavage assay with active recombinant caspase 7 protein. Reaction mixtures were then resolved on SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Reaction mixtures containing full-length YY1 and YY1Δ119 cleavage product were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-YY1 C20 (upper panel). HeLa control (lane 5) and apoptotic (lane 6) WCEs were loaded on the same gel as positive controls. The faint additional fragment in lanes 3 and 4 is an artifact, since it was not observed in apoptotic HeLa WCEs (lane 6). The in vitro samples analyzed in the upper panel (lanes 1 to 4) were separated by PAGE and blotted with the anti-YY1 (pS118) to distinguish the phosphorylated form of YY1 at S118 from the unphosphorylated YY1, as shown in the lower panel. (B) pEGFP-YY1 (WT), nonphosphorylatable mutant pEGFP-YY1 (S118A), empty pEGFP vector, and the transfection control were expressed transiently in HeLa cells. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were either left untreated or were treated with 1 μM STS for 5 h. Samples were separated by PAGE for Western analysis using the anti-GFP antibody to distinguish the recombinant YY1 from endogenous proteins. The antibody detected the Fl-tagged YY1 as well as the N-terminally EGFP-tagged YY1 apoptotic fragments cleaved from the tagged overexpressed YY1 protein. Fl, full length. The blot shown was stripped and analyzed for PARP cleavage, a well-known caspase substrate, using an anti-PARP antibody. Fl-PARP, full-length PARP; t-PARP, truncated PARP; NS, nonspecific. Also, the blot was stripped and hybridized with anti-GAPDH as a loading control.