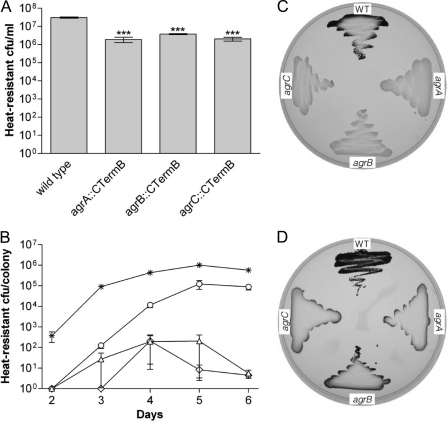
Fig 3.
Sporulation and granulose accumulation in C. acetobutylicum agr mutants. (A) Sporulation assays of wild-type C. acetobutylicum and agr mutants cultured in CBM-S broth for 5 days. The values shown are the means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) of results from ≥3 clones of each strain (each clone representing an independently derived mutant). All values are significantly different from the wild-type strain (***, P < 0.001). (B) The number of heat-resistant endospores formed per colony was determined for C. acetobutylicum (asterisks) and the mutant strains agrA::CTermB (triangles), agrB::CTermB (circles), and agrC::CTermB (diamonds) over a time course of 6 days. The values shown are the means ± SEM of results from 10 colonies of each strain and time point. Mutant strains and wild type are significantly different in all given time points (P < 0.001). (C and D) Granulose assays. Wild-type C. acetobutylicum (WT), agrA::CTermB (agrA), agrB::CTermB (agrB), and agrC::CTermB (agrC) were grown on CBM-G plates and assayed for granulose formation after 24 h (C) and 48 h (D).