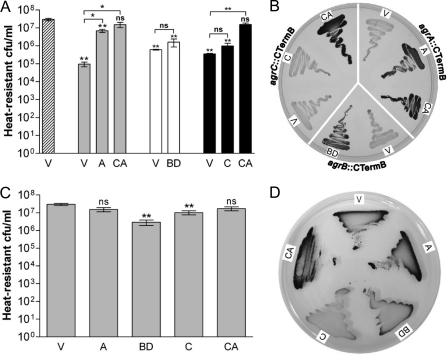
Fig 4.
Complementation of C. acetobutylicum agr mutants and effect of overexpression of agr genes. (A and B) For complementation studies, strains agrA::CTermB (gray bars), agrB::CTermB (white bars), and agrC::CTermB (black bars) were transformed with the vector control (V) or the indicated complementation vectors carrying the agrA (A), agrBD (BD), agrC (C), and agrCA (CA) genes. As a control, the wild-type strain carrying the vector control (striped bar) was also included. Sporulation assays were performed after 5 days in CBM-S broth (A) and granulose accumulation was assayed on CBM-G plates after 24 h (B). The data obtained for mutant strains carrying either a complementation vector or the empty plasmid were compared to those for the wild-type strain harboring the empty vector; significance levels are indicated immediately above the bars. The significance levels of the differences between complemented mutants and the corresponding mutant strains transformed with empty vector are indicated above the brackets: **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant. (C and D) Wild-type agr genes were introduced into the parent C. acetobutylicum strain to investigate the effect of overexpression of these genes on sporulation after 5 days (C) and granulose formation after 24 h (D). The values shown are the means ± standard errors of the means of results from ≥3 independent experiments. The data shown in panel C were compared to those for the wild-type strain carrying the empty plasmid, and the significance levels are indicated: **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant.