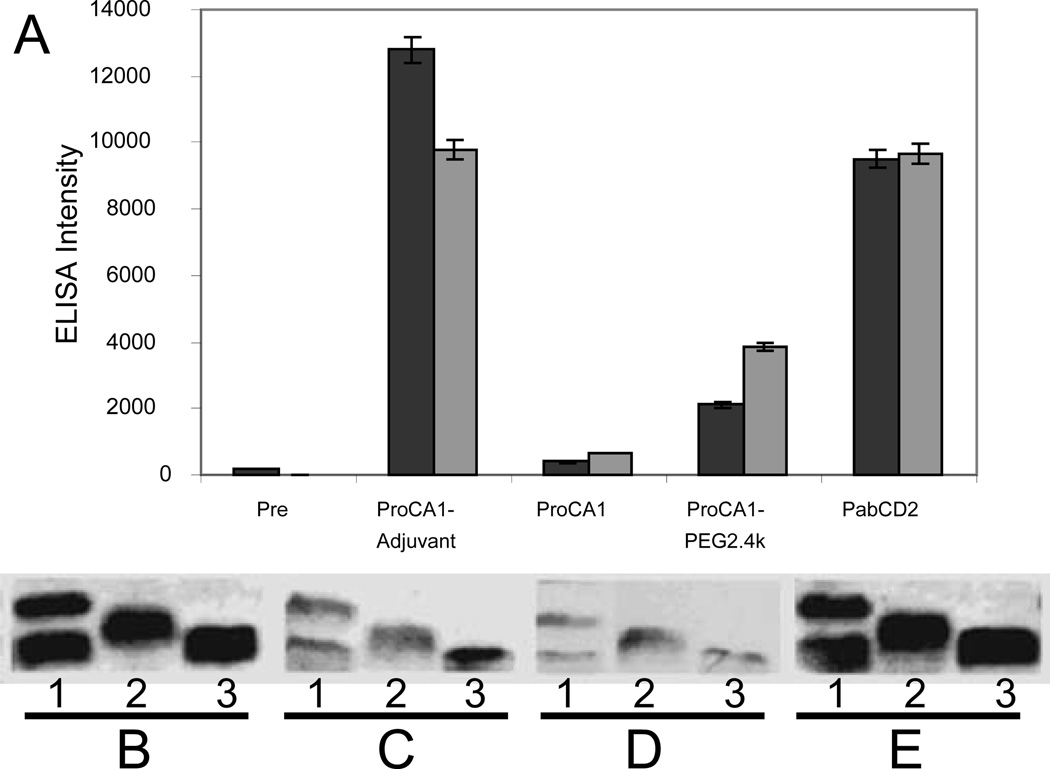
Fig. 6.
(A) ELISA of antibody produced in rabbit serum before (Pre) and weeks 3 (black) and 6 (grey) after intraperitoneal injection of ProCA1 and ProCA1-PEG2.4k mixed with adjuvant (ProCA1-Adjuvant) or with saline buffer (ProCA1). PabCD2 is the anti-serum from rabbits produced by CD2 (commercial source) as an antigen. PEGylation substantially reduced the immune response monitored by poly-antibodies. Antibody generation against the protein contrast agent (both PEGylated and native protein) in the rabbits was examined by Western Blotting. SDS-PAGE shows ProCA1-PEG2.4k (1), ProCA1-PEG0.6k (2) and ProCA1 (3) detected by anti-serum collected from immunoinoculated rabbits. PabCD2 was used as a positive control (E). The other antiserum was prepared from the blood collected after two subsequent injections of native protein ProCA1 mixed with adjuvant (B). ProCA1 in the absence of adjuvant (C). ProCA1-PEG2.4k mixed in absence of adjuvant (D). The results showe that addition of adjuvant induced stronger immune responses (B). PEGylation modifications of the protein dramatically reduced immune responses in the rabbits (D). Our results suggest that the immunogenecity of the protein contrast agent may not be very strong, especially without addition of adjuvant.