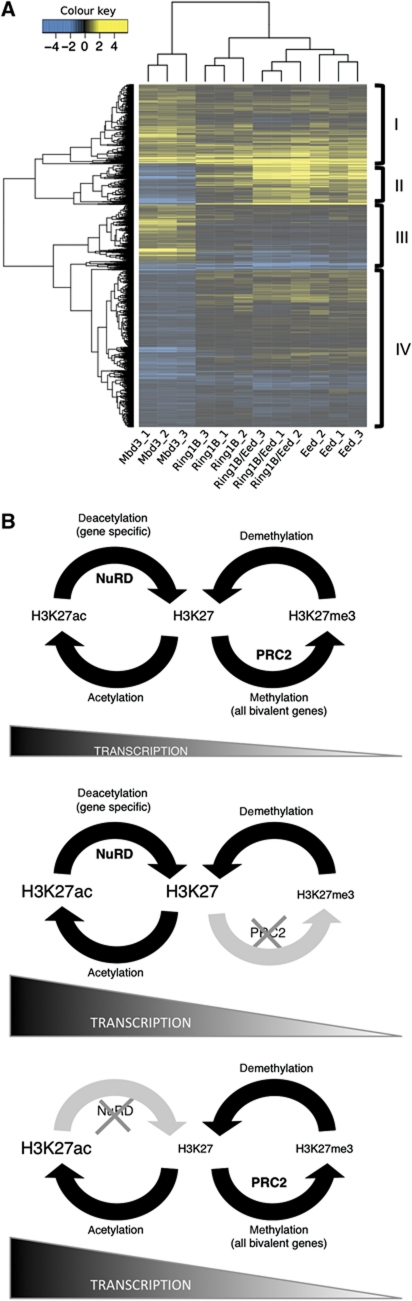
Figure 7.
Overlap of NuRD and PRC function in gene regulation. (A) Expression patterns of genes differentially expressed between wild-type and Mbd3−/− ES cells (P<0.05) were assessed in data from Leeb et al (2010) describing gene expression changes in PRC mutant ES cells. A total of 2907 probe sets were found to be differentially expressed between the reference and Mbd3 mutant samples, mapping to 1967 unique genes using the re-annotated array information provided by Leeb et al. Of these, 1879 genes were also present on the Leeb microarray platform, although not necessarily differentially expressed. The log2 fold change of these genes relative to their respective wild-type samples is illustrated in the figure. Genes showing reduced expression compared with wild-type cells are indicated in blue; those showing increased expression are indicated in yellow. Mbd3_1, Mbd3_2 and Mbd3_3 indicate results from three different Mbd3−/− ES cell samples corresponding to two independently derived ES cell lines. Ring1B_1-3, Eed_1-3 and Ring1B/Eed_1-3 represent results from three replicates each of Ring1B-null ES cells, Eed-null ES cells and Ring1B/Eed-double null ES cells, respectively (Leeb et al, 2010). Where multiple probes map to the same gene, only the probe displaying the largest deviation from the reference sample is included here. The four main gene clusters are indicated on the right hand side (I–IV). (B) Two-step model for control of transcription illustrating relationship between acetylation status, here controlled by NuRD, and methylation of H3K27 by PRC2. Top panel: in wild-type cells, PRC2 and NuRD function fully. NuRD directs deacetylation of specific genes, which then become available for trimethylation by PRC2. Middle panel: in cells lacking functional PRC2, for example, Eed−/− cells, H3K27 trimethylation is lost genome-wide, the balance moves towards the acetylation/deacetylation cycle and transcription of bivalent genes increases overall. Bottom panel: in the absence of NuRD, deacetylation fails to occur at specific loci only. At these genes, there is an increase in acetylation, a subsequent reduction in trimethylation at H3K27 through loss of substrate for PRC2 and an increase in transcription.