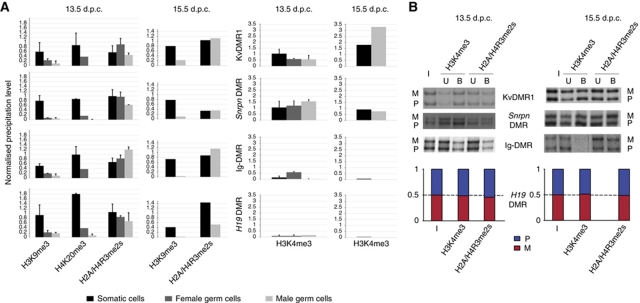
Figure 3.
Reprogramming of histone methylation at ICRs in PGCs. (A) To the left, quantification of H3K9me3, H4K20me3, and H2A/H4R3me2s in male (white) and female (grey) PGCs and somatic control cells (black; a mixture of male and female cells). Relative enrichment is defined as the ratio between the bound (with subtracted background) and the input chromatin, and was normalised to the (bound-background)/input ratio obtained for IAP elements. To the right, quantification of H3K4me3. Relative enrichment was calculated as the ratio between the bound fraction (with subtracted background) and input and was normalised to the (bound-background)/input ratio obtained for Rpl30. Experiments were performed at least in triplicate. Standard deviations are not given for experiments at 15.5 d.p.c., which were performed twice on male PGCs. Female PGCs were not analysed by ChIP at 15.5 d.p.c. (B) PCR-SSCP analysis (KvDMR1, Snrpn DMR, Ig-DMR) or real-time PCR-based allelic discrimination (H19 DMR) after cChIP on male germ cells. At all four ICRs analysed, the histone methylations studied were similarly precipitated from the maternal (M) and the paternal (P) alleles (the ratio between the parental alleles were in all cases smaller than 1.5). In this qualitative assay, the PCR amplifications were close to saturation.