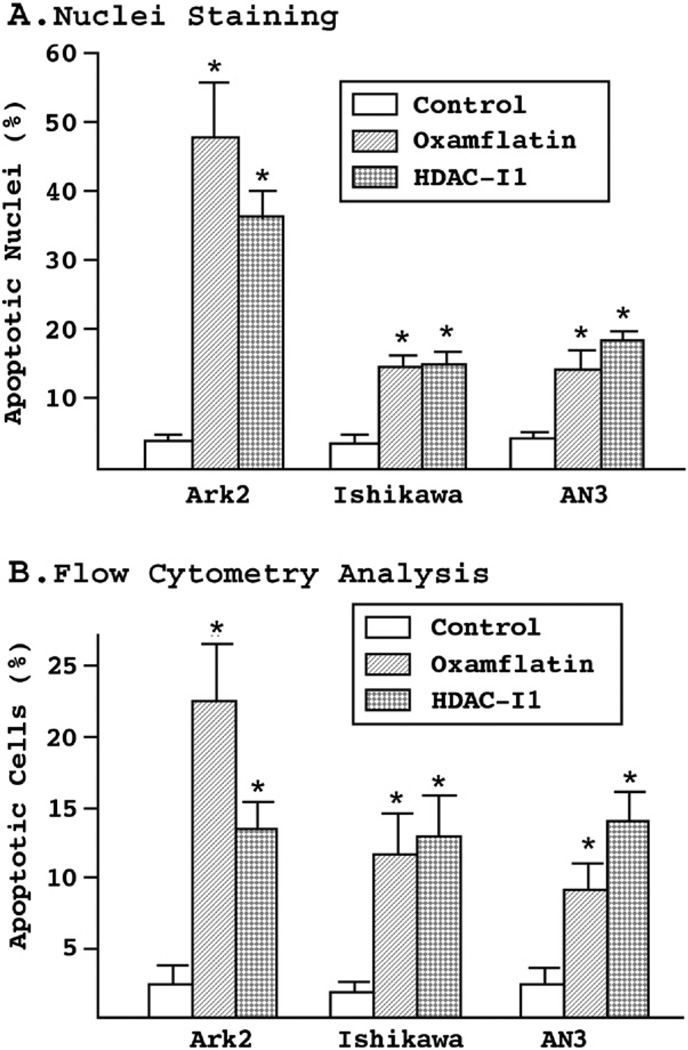
Figure 3.
(A) Nuclei staining assay. The three endometrial cancer cell lines were treated with oxamflatin (0.5 μM) and HDAC-I1 (1.0 μM) for 3 days. Nuclei condensation and fragmentation were detected by Hoechst staining of genomic DNA. Depending on cell type and drug used, a three- to nine-fold increase in apoptotic nuclei was observed. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of cell apoptosis. Following three days of treatment with oxamflatin (0.25 μM) and HDAC-I1 (0.5 μM), the cells were stained with biotin-labeled Annexin V and apoptotic cells counted by flow cytometry. The results confirm significant cell death induced by oxamflatin and HDAC-I1 treatment. Similar drug sensitivity profiles to those observed in cell growth experiments (Fig. 1) were found in the nuclei staining and flow cytometry experiments. Statistical significance between experimental and control groups (p<0.05) is marked by asterisks on the top of standard error bars.