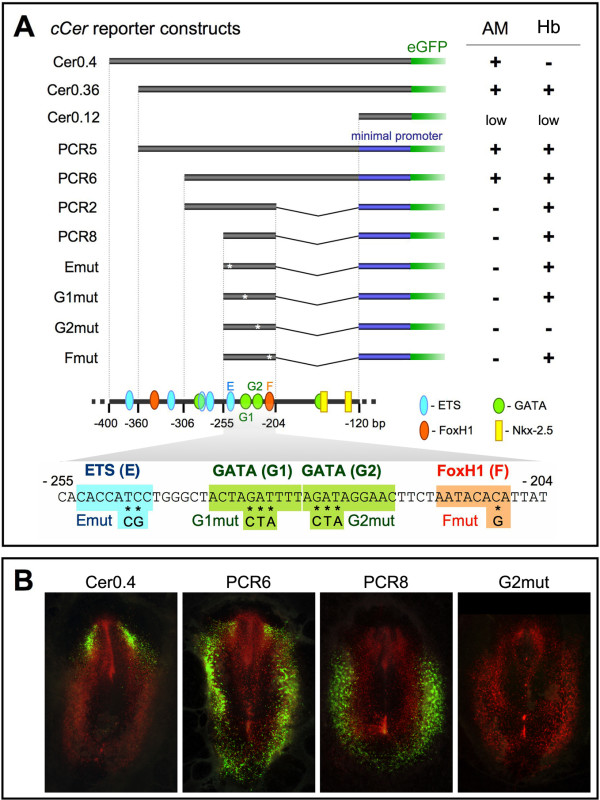
Figure 1.
Identification of the cCer hemangioblast enhancer. (A) Enhancer analysis of the cCer cis-regulatory region. cCer 5' genomic sequences (black boxes) were either directly fused to the eGFP reporter gene (green boxes) or sub-cloned into an enhancerless vector carrying the human β-globin minimal promoter (dark blue boxes) upstream of the eGFP coding sequence. Emut, G1mut, G2mut and Smut constructs were designed by introducing mutations in the ETS, GATA (G1 and G2) or FoxH1 (F) binding elements of the PCR8 sequence, respectively (asterisks; see sequence below). The presence ("+") or absence ("-") of eGFP expression in the anterior mesendoderm (AM) and in hemangioblasts (Hb) of electroporated chick embryos is listed on the right. Each result is representative of at least 12 embryos. A schematic representation of cCer -400 to -120 bp regulatory region and the nucleotide sequence of the PCR8 fragment (-255 to -204 bp) are shown in the bottom. Binding sites for the transcription factors ETS (E; blue), GATA (G1 and G2; green), FoxH1 (F; orange) and Nkx-2.5 (yellow) are outlined. The ETS site in the -400 to -360 bp silencing region may be responsible for the repression of hemangioblast expression, whereas the two Nkx-2.5 sites in the -204 to -120 bp sequence may regulate anterior mesendoderm expression. Mutations introduced into the E, G1, G2 and F sites of the Emut, G1mut, G2mut and Smut constructs are also indicated in the PCR8 sequence. (B) Cer-eGFP reporter expression in electroporated chick embryos. Embryos were co-transfected with pCAGGS-RFP (positive control; red fluorescence) and each Cer-eGFP reporter construct (green fluorescence) at stage HH3 and fixed at HH6. Examples of electroporated embryos with ubiquitous RFP fluorescence and specific eGFP expression in the AM (Cer0.4), AM and Hb (PCR6), and Hb alone (PCR8), or without eGFP expression (G2mut).